Comparator pH study to evaluate the single-dose pharmacodynamics of dual delayed-release dexlansoprazole 60 mg and delayed-release esomeprazole 40 mg
- PMID: 22016582
- PMCID: PMC3190289
- DOI: 10.2147/CEG.S24063
Comparator pH study to evaluate the single-dose pharmacodynamics of dual delayed-release dexlansoprazole 60 mg and delayed-release esomeprazole 40 mg
Erratum in
-
Erratum: corrigendum.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2011;4:255. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S26569. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 22162928 Free PMC article.
Abstract
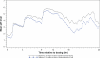
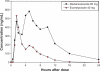
Background: This paper describes a Phase 1, single-center, randomized, open-label, two-period crossover study which compared the pharmacodynamic effects of single doses of dexlansoprazole modified-release 60 mg and esomeprazole 40 mg on 24-hour intragastric pH in healthy adult subjects.
Methods: Forty-four subjects aged 20-54 years were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to two sequence groups defining the order in which they received dexlansoprazole and esomeprazole in periods 1 and 2. Primary pharmacodynamic end points over 24 hours postdose were percentage of time with intragastric pH > 4 and mean pH, and secondary pharmacodynamic end points were percentage of time intragastric pH > 4, and mean pH at 0-12 hours, and at >12-24 hours postdose. Each drug was given after an overnight fast and one hour before breakfast. Continuous pH recording began immediately before dosing through to 24 hours postdose.
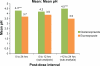
Results: At 0-24 hours postdose, the mean percentage of time with pH > 4 for dexlansoprazole and esomeprazole was 58% and 48%, respectively; the difference was statistically significant (P = 0.003). The average of mean pH values at 0-24 hours postdose for dexlansoprazole and esomeprazole were 4.3 and 3.7, respectively; the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.001). At >12-24 hours postdose, mean percentage of time with pH > 4 and average of mean pH were greater for dexlansoprazole (60% and 4.5, respectively) compared with esomeprazole (42% and 3.5, respectively); the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.001 for both intervals). At 0-12 hours postdose, the difference in dexlansoprazole and esomeprazole values for the pharmacodynamic end points was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: For the entire 24-hour postdose period, predominantly resulting from the >12-24-hour postdose interval, the average intragastric pH following a single dose of dexlansoprazole 60 mg was higher compared with that observed following a single dose of esomeprazole 40 mg, and the difference was statistically significant.
Keywords: TAK-390MR; esomeprazole; intragastric pH; pharmacokinetics; proton pump inhibitor; single dose.
Figures

References
-
- DeVault KR, Talley NJ. Insights into the future of gastric acid suppression. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6:524–532. - PubMed
-
- Vakily M, Zhang W, Wu J, Atkinson SN, Mulford D. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a known active PPI with a novel dual delayed release technology, dexlansoprazole MR: A combined analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009;25:627–638. - PubMed
-
- Metz DC, Vakily M, Dixit T, Mulford D. Review article: Dual delayed release formulation of dexlansoprazole MR, a novel approach to overcome the limitations of conventional single release proton pump inhibitor therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009;29:928–937. - PubMed
-
- Deerfield, IL: Takeda Pharmaceuticals America Inc; 2011. Dexilant® (dexlansoprazole) delayed release capsules [package insert]
-
- Wilmington, DE: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP; 2011. Nexium® (esomeprazole magnesium) delayed-release capsules [package insert]
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

