Relation between ABO blood groups and Helicobacter pylori infection in symptomatic patients
- PMID: 22016583
- PMCID: PMC3190290
- DOI: 10.2147/CEG.S23019
Relation between ABO blood groups and Helicobacter pylori infection in symptomatic patients
Abstract
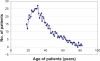
Epidemiological studies have demonstrated higher frequencies of the O blood group and the nonsecretor phenotype of ABH antigens among patients suffering from peptic ulcers. Since Helicobacter pylori has been established as the main etiological factor in this disease, controversies about the associations of the ABO and Lewis blood group phenotypes and secretor and nonsecretor phenotypes in relation to susceptibility towards infection by this bacillus have been presented. The aim of this study was to verify the frequencies of ABO and Rhesus (Rh) blood groups in H. pylori seropositive symptomatic patients. The study included (n = 1108) patients with dyspepsia symptoms referred from an outpatient clinic in Erbil city for investigation. Age, sex, and residency were recorded as a routine laboratory framework. Patients underwent SD Bioline (Standard Diagnostics Inc, Kyonggi-do, South Korea) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay serologic tests for H. pylori. ABO blood group phenotypes were determined by a standard hemagglutination test. Results showed that 64.8% of patients (n = 718/1108) were seropositive for H. pylori infection, and (35.2%) (n = 390/1108) were seronegative. Of the seropositive patients, 40.8% (n = 293/718) were male and 59.2% (n = 425/718) were female; while of the seronegative patients, 46.7% (n = 182/390) were male and 53.3% (n = 208/390) were female. The mean age for seropositives and seronegatives was (38.0 ± 14.6) years and (37.6 ± 15.7) years respectively. The frequency of the ABO and Rh-positive (Rh+) blood groups among seropositive patients was (A = 32.0%, B = 19.5%, AB = 6.7%, O = 41.8%, and Rh+ = 92.5%) and was (A = 32.3%, B = 28.2%, AB = 8.0%, O = 31.5%, and Rh+ = 92.5%) in seronegatives. The results of this study suggest that ABO blood groups, age, and gender influence seropositivity for H. pylori infection.
Keywords: H. pylori; age; prevalence; seropositive; sex.
Figures
References
-
- Mourant AE, Kopec AC, Domaniewska-Sobczak K. Blood Groups and Diseases: A Study of Associations of Diseases with Blood Groups and Other Polymorphisms. London: Oxford University Press; 1978.
-
- Jaff MS, O’Brian DS. Excess of blood group B in primary myelofibrosis. Vox Sang. 1987;52:250–253. - PubMed
-
- Marshall BJ. Campylobacter pyloridis and gastritis. J Infect Dis. 1986;153:650–658. - PubMed
-
- Tytgat GNJ, Axon ATR, Dixon MF, Graham DY, Lee A, Marshall BJ. London: Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1990. Helicobacter pylori, causal agent in peptic ulcer disease. Working party reports 1990; pp. 36–45.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources