New user-friendly approach to obtain an Eisenberg plot and its use as a practical tool in protein sequence analysis
- PMID: 22016610
- PMCID: PMC3189734
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12095577
New user-friendly approach to obtain an Eisenberg plot and its use as a practical tool in protein sequence analysis
Abstract
The Eisenberg plot or hydrophobic moment plot methodology is one of the most frequently used methods of bioinformatics. Bioinformatics is more and more recognized as a helpful tool in Life Sciences in general, and recent developments in approaches recognizing lipid binding regions in proteins are promising in this respect. In this study a bioinformatics approach specialized in identifying lipid binding helical regions in proteins was used to obtain an Eisenberg plot. The validity of the Heliquest generated hydrophobic moment plot was checked and exemplified. This study indicates that the Eisenberg plot methodology can be transferred to another hydrophobicity scale and renders a user-friendly approach which can be utilized in routine checks in protein-lipid interaction and in protein and peptide lipid binding characterization studies. A combined approach seems to be advantageous and results in a powerful tool in the search of helical lipid-binding regions in proteins and peptides. The strength and limitations of the Eisenberg plot approach itself are discussed as well. The presented approach not only leads to a better understanding of the nature of the protein-lipid interactions but also provides a user-friendly tool for the search of lipid-binding regions in proteins and peptides.
Keywords: Eisenberg plot; Heliquest; amphitropic proteins; hydrophobic moment plot; lipid binding regions; protein-lipid interactions; transmembrane proteins.
Figures

 ), Surface seeking (
), Surface seeking (
 ) and TransMembrane (■) segments are depicted.
) and TransMembrane (■) segments are depicted.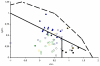
 ), Globular (
), Globular (
 ) and TransMembrane (■) segments are depicted, see Table 1 for details. Examples of signal peptides (SP) (circles, black), lipid-binding peptides (LBP) (circles, blue), amphitropics (circles, green) and others (circles, orange) are depicted, see Table 2 for details.
) and TransMembrane (■) segments are depicted, see Table 1 for details. Examples of signal peptides (SP) (circles, black), lipid-binding peptides (LBP) (circles, blue), amphitropics (circles, green) and others (circles, orange) are depicted, see Table 2 for details.References
-
- Eisenberg D, Weiss RM, Terwilliger TC. The helical hydrophobic moment: A measure of the amphiphilicity of a helix. Nature. 1982;299:371–374. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberg D, Schwarz E, Komaromy M, Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984;15:125–142. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberg D. Three-dimensional structure of membrane and surface proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:595–623. - PubMed
-
- Phoenix DA, Harris F. The hydrophobic moment and its use in the classification of amphiphilic structures (review) Mol Membr Biol. 2002;19:1–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

