Molecularly imprinted polymers: present and future prospective
- PMID: 22016636
- PMCID: PMC3189760
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12095908
Molecularly imprinted polymers: present and future prospective
Abstract
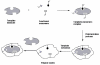
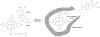
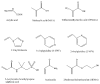
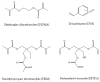
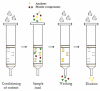
Molecular Imprinting Technology (MIT) is a technique to design artificial receptors with a predetermined selectivity and specificity for a given analyte, which can be used as ideal materials in various application fields. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs), the polymeric matrices obtained using the imprinting technology, are robust molecular recognition elements able to mimic natural recognition entities, such as antibodies and biological receptors, useful to separate and analyze complicated samples such as biological fluids and environmental samples. The scope of this review is to provide a general overview on MIPs field discussing first general aspects in MIP preparation and then dealing with various application aspects. This review aims to outline the molecularly imprinted process and present a summary of principal application fields of molecularly imprinted polymers, focusing on chemical sensing, separation science, drug delivery and catalysis. Some significant aspects about preparation and application of the molecular imprinting polymers with examples taken from the recent literature will be discussed. Theoretical and experimental parameters for MIPs design in terms of the interaction between template and polymer functionalities will be considered and synthesis methods for the improvement of MIP recognition properties will also be presented.
Keywords: HPLC; artificial receptors; catalysis; drug delivery; molecular imprinting technology (MIT); molecular recognition; molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs); sensors; solid phase extraction.
Figures

References
-
- Takagishi T, Klotz IM. Macromolecule-small molecule interactions; introduction of additional binding sites in polyethyleneimine by disulfide cross-linkages. Biopolymers. 1972;11:483–491. - PubMed
-
- Wulff G, Sarhan A. Use of polymers with enzyme-analogous structures for the resolution of racemates. Angew Chem Int Ed. 1972;11:341–342.
-
- Mosbach K, Ramström O. The emerging technique of molecular imprinting and its future impact on biotechnology. Nat Biotechnol. 1996;14:163–170.
-
- Whitcombe MJ, Alexander C, Vulfson EN. Smart polymers for the food industry. Trends Food Sci Technol. 1997;8:140–145.
-
- Yan S, Fang Y, Gao Z. Quartz crystal microbalance for the determination of daminozide using molecularly imprinted polymers as recognition element. Biosens Bioelectron. 2007;22:1087–1091. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

