Skeletal muscle na channel disorders
- PMID: 22016737
- PMCID: PMC3192954
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2011.00063
Skeletal muscle na channel disorders
Abstract
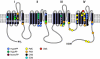
Five inherited human disorders affecting skeletal muscle contraction have been traced to mutations in the gene encoding the voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v)1.4. The main symptoms of these disorders are myotonia or periodic paralysis caused by changes in skeletal muscle fiber excitability. Symptoms of these disorders vary from mild or latent disease to incapacitating or even death in severe cases. As new human sodium channel mutations corresponding to disease states become discovered, the importance of understanding the role of the sodium channel in skeletal muscle function and disease state grows.
Keywords: Nav1.4; skeletal muscle; sodium channel; treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A sodium channel knockin mutant (NaV1.4-R669H) mouse model of hypokalemic periodic paralysis.J Clin Invest. 2011 Oct;121(10):4082-94. doi: 10.1172/JCI57398. Epub 2011 Sep 1. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21881211 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Channelopathies of Skeletal Muscle.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018;246:309-330. doi: 10.1007/164_2017_52. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28939973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human voltage-gated sodium channel mutations that cause inherited neuronal and muscle channelopathies increase resurgent sodium currents.J Clin Invest. 2010 Jan;120(1):369-78. doi: 10.1172/JCI40801. Epub 2009 Dec 28. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 20038812 Free PMC article.
-
N1366S mutation of human skeletal muscle sodium channel causes paramyotonia congenita.J Physiol. 2017 Nov 15;595(22):6837-6850. doi: 10.1113/JP274877. Epub 2017 Oct 15. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28940424 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium channelopathies of skeletal muscle result from gain or loss of function.Pflugers Arch. 2010 Jul;460(2):239-48. doi: 10.1007/s00424-010-0814-4. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Pflugers Arch. 2010. PMID: 20237798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Blockers of Skeletal Muscle Nav1.4 Channels: From Therapy of Myotonic Syndrome to Molecular Determinants of Pharmacological Action and Back.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):857. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010857. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A case of paramyotonia congenita in pregnancy.Obstet Med. 2020 Dec;13(4):192-194. doi: 10.1177/1753495X18816171. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Obstet Med. 2020. PMID: 33343696 Free PMC article.
-
[I1363T mutation induces the defects in fast inactivation of human skeletal muscle voltage-gated sodium channel].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019 May 25;48(1):12-18. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2019.02.03. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019. PMID: 31102352 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Keeping hyperactive voltage-gated sodium channels in silent mode.J Physiol. 2012 Jun 1;590(11):2543-4. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.229310. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22787162 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Divergent cis-regulatory evolution underlies the convergent loss of sodium channel expression in electric fish.Sci Adv. 2022 Jun 3;8(22):eabm2970. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm2970. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35648851 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almers W. (1980). Potassium concentration changes in the transverse tubules of vertebrate skeletal muscle. Fed. Proc. 39, 1527–1532 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

