Sustained release myofascial release as treatment for a patient with complications of rheumatoid arthritis and collagenous colitis: a case report
- PMID: 22016756
- PMCID: PMC3184472
- DOI: 10.3822/ijtmb.v4i3.112
Sustained release myofascial release as treatment for a patient with complications of rheumatoid arthritis and collagenous colitis: a case report
Abstract
Background: Myofascial release (MFR) is a manual therapeutic technique used to release fascial restrictions, which may cause neuromusculoskeletal and systemic pathology.
Purpose: This case report describes the use of sustained release MFR techniques in a patient with a primary diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and a secondary diagnosis of collagenous colitis. Changes in pain, cervical range of motion, fatigue, and gastrointestinal tract function, as well as the impact of RA on daily activities, were assessed.
Methods: A 54-year-old white woman presented with signs and symptoms attributed to RA and collagenous colitis. Pre and post measurements were taken with each treatment and during the interim between the initial and final treatment series. The patient recorded changes in pain, fatigue, gastrointestinal tract function, and quality of life. Cervical range of motion was assessed. Six sustained release MFR treatment sessions were provided over a 2-week period. Following an 8-week interim, two more treatments were performed.
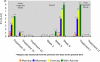
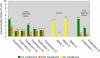
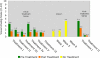
Results: The patient showed improvements in pain, fatigue, gastrointestinal tract function, cervical range of motion, and quality of life following the initial treatment series of six sessions. The patient maintained positive gains for 5 weeks following the final treatment, after which her symptoms returned to near baseline measurements. Following two more treatments, positive gains were achieved once again.
Conclusions: In a patient with RA and collagenous colitis, the application of sustained release MFR techniques in addition to standard medical treatment may provide short-term and long-term improvements in comorbid symptoms and overall quality of life.
Keywords: Myofascial release; inflammatory bowel disease; manual therapy; rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improvement in clinical outcomes after dry needling versus myofascial release on pain pressure thresholds, quality of life, fatigue, pain intensity, quality of sleep, anxiety, and depression in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome.Disabil Rehabil. 2019 Sep;41(19):2235-2246. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2018.1461259. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Disabil Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 29681188 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of direct vs indirect technique myofascial release in the management of tension-type headache.J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2011 Oct;15(4):431-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2011.01.021. Epub 2011 Feb 11. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2011. PMID: 21943616 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of myofascial release in the management of plantar heel pain: a randomized controlled trial.Foot (Edinb). 2014 Jun;24(2):66-71. doi: 10.1016/j.foot.2014.03.005. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Foot (Edinb). 2014. PMID: 24703512 Clinical Trial.
-
Celecoxib: a review of its use in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and acute pain.Drugs. 2000 Apr;59(4):957-80. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200059040-00017. Drugs. 2000. PMID: 10804043 Review.
-
Collagenous colitis and rheumatoid arthritis with response to sulfasalazine. A case report and review of the literature.J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987 Aug;9(4):456-60. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198708000-00020. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1987. PMID: 2888802 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence-based pain management: is the concept of integrative medicine applicable?EPMA J. 2012 Oct 22;3(1):13. doi: 10.1186/1878-5085-3-13. EPMA J. 2012. PMID: 23088743 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation of the CARE Guidelines for Therapeutic Massage and Bodywork Publications: Efforts To Improve the Impact of Case Reports.Int J Ther Massage Bodywork. 2014 Sep 3;7(3):32-40. doi: 10.3822/ijtmb.v7i3.251. eCollection 2014 Sep. Int J Ther Massage Bodywork. 2014. PMID: 25184013 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Integrative Naturopathy and Yoga in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated with Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertension.Anc Sci Life. 2017 Jan-Mar;36(3):163-166. doi: 10.4103/asl.ASL_80_16. Anc Sci Life. 2017. PMID: 28867861 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of electro-acupuncture, massage, mud, and sauna therapies in patient with rheumatoid arthritis.J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2015 Oct-Dec;6(4):295-9. doi: 10.4103/0975-9476.172415. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2015. PMID: 26834431 Free PMC article.
-
Celebrating the 10th Anniversary of the International Journal of Therapeutic Massage and Bodywork.Int J Ther Massage Bodywork. 2018 Aug 5;11(3):1-3. eCollection 2018 Aug. Int J Ther Massage Bodywork. 2018. PMID: 30108666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goodman CC, Boissonnault WG, Fuller KS. Pathology: Implications for the Physical Therapist. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders; 2003. pp. 646–650.pp. 946–954.
-
- Silber JS, Verma RB, Greenberg AS. Rheumatoid arthritis of the cervical spine. Neurosurg Q. 2006;16(1):1–8. doi: 10.1097/01.wnq.0000203278.74526.79. - DOI
-
- Fukase M, Koizumi F, Wakaki K. Histopathologic analysis of 16 subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1980;30:871–882. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
