Plasmid metagenome reveals high levels of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements in activated sludge
- PMID: 22016806
- PMCID: PMC3189950
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026041
Plasmid metagenome reveals high levels of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements in activated sludge
Abstract
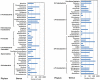
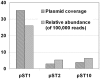
The overuse or misuse of antibiotics has accelerated antibiotic resistance, creating a major challenge for the public health in the world. Sewage treatment plants (STPs) are considered as important reservoirs for antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) and activated sludge characterized with high microbial density and diversity facilitates ARG horizontal gene transfer (HGT) via mobile genetic elements (MGEs). However, little is known regarding the pool of ARGs and MGEs in sludge microbiome. In this study, the transposon aided capture (TRACA) system was employed to isolate novel plasmids from activated sludge of one STP in Hong Kong, China. We also used Illumina Hiseq 2000 high-throughput sequencing and metagenomics analysis to investigate the plasmid metagenome. Two novel plasmids were acquired from the sludge microbiome by using TRACA system and one novel plasmid was identified through metagenomics analysis. Our results revealed high levels of various ARGs as well as MGEs for HGT, including integrons, transposons and plasmids. The application of the TRACA system to isolate novel plasmids from the environmental metagenome, coupled with subsequent high-throughput sequencing and metagenomic analysis, highlighted the prevalence of ARGs and MGEs in microbial community of STPs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Zhang XX, Zhang T, Fang HHP. Antibiotic resistance genes in water environment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009;82:397–414. - PubMed
-
- Szczepanowski R, Krahn I, Linke B, Goesmann A, Pühler A, et al. Antibiotic multiresistance plasmid pRSB101 isolated from a wastewater treatment plant is related to plasmids residing in phytopathogenic bacteria and carries eight different resistance determinants including a multidrug transport system. Microbiology. 2004;150:3613–30. - PubMed
-
- Tennstedt T, Szczepanowski R, Krahn K, Pühler A, Schlüter A. Sequence of the 68,869 bp IncP-1α plasmid pTB11 from a waste-water treatment plant reveals a highly conserved backbone, a Tn402-like integron and other transposable elements. Plasmid. 2005;53:218–238. - PubMed
-
- da Silva MF, Vaz-Moreira I, Gonzalez-Pajuelo M, Nunes OC, Manaia CM. Antimicrobial resistance patterns in Enterobacteriaceae isolated from an urban wastewater treatment plant. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2007;60:166–176. - PubMed
-
- Taviani E, Ceccarelli D, Lazaro N, Bani S, Cappuccinelli P, met al. Environmental Vibrio spp., isolated in Mozambique, contain a polymorphic group of integrative conjugative elements and class 1 integrons. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2008;64:45–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

