Expanding roles of ZEB factors in tumorigenesis and tumor progression
- PMID: 22016835
- PMCID: PMC3196287
Expanding roles of ZEB factors in tumorigenesis and tumor progression
Abstract
The ZEB family of transcription factors regulates key factors during embryonic development and cell differentiation but their role in cancer biology has only more recently begun to be recognized. Early evidence showed that ZEB proteins induce an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition linking their expression with increased aggressiveness and metastasis in mice models and a wide range of primary human carcinomas. Reports over the last few years have found that ZEB proteins also play critical roles in the maintenance of cancer cell stemness, control of replicative senescence, tumor angiogenesis, overcoming of oncogenic addiction and resistance to chemotherapy. These expanding roles in tumorigenesis and tumor progression set ZEB proteins as potential diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Cancer; E-cadherin; EMT; ZEB1; ZEB2; cancer stem cells; chemotherapy resistance; transcription; tumor invasiveness.
Figures
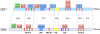



References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Polyak K, Weinberg RA. Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:265–273. - PubMed
-
- Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A. Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:415–428. - PubMed
-
- Moreno-Bueno G, Portillo F, Cano A. Transcriptional regulation of cell polarity in EMT and cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:6958–6969. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
