The pathogenesis of mixed-lineage leukemia
- PMID: 22017583
- PMCID: PMC3381338
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011811-132434
The pathogenesis of mixed-lineage leukemia
Abstract
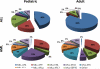
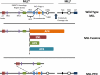
Aggressive leukemias arise in both children and adults as a result of rearrangements to the mixed-lineage leukemia gene (MLL) located on chromosome 11q23. MLL encodes a large histone methyltransferase that directly binds DNA and positively regulates gene transcription, including homeobox (HOX) genes. MLL is involved in chromosomal translocations, partial tandem duplications, and amplifications, all of which result in hematopoietic malignancies due to sustained HOX expression and stalled differentiation. MLL lesions are associated with both acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoid leukemia and are usually associated with a relatively poor prognosis despite improved treatment options such as allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, which underscores the need for new treatment regimens. Recent advances have begun to reveal the molecular mechanisms that drive MLL-associated leukemias, which, in turn, have provided opportunities for therapeutic development. Here, we discuss the etiology of MLL leukemias and potential directions for future therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Djabali M, Selleri L, Parry P, Bower M, Young BD, Evans GA. A trithorax-like gene is interrupted by chromosome 11q23 translocations in acute leukaemias. Nat Genet. 1992;2:113–8. - PubMed
-
- Gu Y, Nakamura T, Alder H, Prasad R, Canaani O, Cimino G, Croce CM, Canaani E. The t(4;11) chromosome translocation of human acute leukemias fuses the ALL-1 gene, related to Drosophila trithorax, to the AF-4 gene. Cell. 1992;71:701–8. - PubMed
-
- Tkachuk DC, Kohler S, Cleary ML. Involvement of a homolog of Drosophila trithorax by 11q23 chromosomal translocations in acute leukemias. Cell. 1992;71:691–700. - PubMed
-
- Krivtsov AV, Armstrong SA. MLL translocations, histone modifications and leukaemia stem-cell development. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:823–33. - PubMed
-
- Hess JL. MLL: a histone methyltransferase disrupted in leukemia. Trends Mol Med. 2004;10:500–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

