Krüppel-like factor 4 is induced by rapamycin and mediates the anti-proliferative effect of rapamycin in rat carotid arteries after balloon injury
- PMID: 22017667
- PMCID: PMC3413870
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01734.x
Krüppel-like factor 4 is induced by rapamycin and mediates the anti-proliferative effect of rapamycin in rat carotid arteries after balloon injury
Abstract
Background and purpose: The transcription factor, Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4), plays an important role in regulating the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. This study aimed to examine the effect of rapamycin on the expression of KLF4 and the role of KLF4 in arterial neointimal formation.
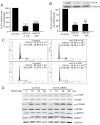
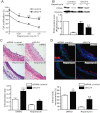
Experimental approach: Expression of KLF4 was monitored using real-time PCR and immunoblotting in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. and in rat carotid arteries in vivo after balloon injury. Adenovirus-mediated overexpression and siRNA-mediated knockdown of KLF4 were used to examine the role of KLF4 in mediating the anti-proliferative role of rapamycin . KLF4-regulated genes were identified using cDNA microarray.
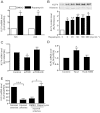
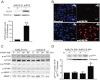
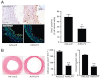
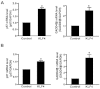
Key results: Rapamycin induced the expression of KLF4 in vitro and in vivo. Overexpression of KLF4 inhibited cell proliferation and the activity of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and its downstream pathways, including 4EBP-1 and p70S6K in vascular smooth muscle cells and prevented the neointimal formation in the balloon-injured arteries. KLF4 up-regulated the expression of GADD45β, p57(kip2) and p27(kip1) . Furthermore, knockdown of KLF4 attenuated the anti-proliferative effect of rapamycin both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions and implications: KLF4 plays an important role in mediating the anti-proliferative effect of rapamycin in VSMCs and balloon-injured arteries. Thus, it is a potential target for the treatment of proliferative vascular disorders such as restenosis after angioplasty.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Adam PJ, Regan CP, Hautmann MB, Owens GK. Positive- and negative-acting Kruppel-like transcription factors bind a transforming growth factor beta control element required for expression of the smooth muscle cell differentiation marker SM22alpha in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:37798–37806. - PubMed
-
- Agrotis A, Kanellakis P, Kostolias G, Di Vitto G, Wei C, Hannan R, et al. Proliferation of neointimal smooth muscle cells after arterial injury. Dependence on interactions between fibroblast growth factor receptor-2 and fibroblast growth factor-9. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:42221–42229. - PubMed
-
- Bayes-Genis A, Campbell JH, Carlson PJ, Holmes DR, Jr, Schwartz RS. Macrophages, myofibroblasts and neointimal hyperplasia after coronary artery injury and repair. Atherosclerosis. 2002;163:89–98. - PubMed
-
- Clowes AW, Reidy MA, Clowes MM. Mechanisms of stenosis after arterial injury. Lab Invest. 1983;49:208–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

