The three-dimensional architecture of a bacterial genome and its alteration by genetic perturbation
- PMID: 22017872
- PMCID: PMC3874842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.09.010
The three-dimensional architecture of a bacterial genome and its alteration by genetic perturbation
Abstract
We have determined the three-dimensional (3D) architecture of the Caulobacter crescentus genome by combining genome-wide chromatin interaction detection, live-cell imaging, and computational modeling. Using chromosome conformation capture carbon copy (5C), we derive ~13 kb resolution 3D models of the Caulobacter genome. The resulting models illustrate that the genome is ellipsoidal with periodically arranged arms. The parS sites, a pair of short contiguous sequence elements known to be involved in chromosome segregation, are positioned at one pole, where they anchor the chromosome to the cell and contribute to the formation of a compact chromatin conformation. Repositioning these elements resulted in rotations of the chromosome that changed the subcellular positions of most genes. Such rotations did not lead to large-scale changes in gene expression, indicating that genome folding does not strongly affect gene regulation. Collectively, our data suggest that genome folding is globally dictated by the parS sites and chromosome segregation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
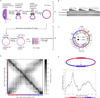
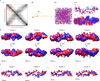
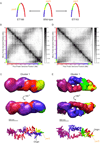
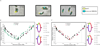
Comment in
-
Bacterial physiology. Seeing Caulobacter in 3D.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 Nov 16;9(12):834-5. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2703. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 22085857 No abstract available.
-
Three-dimensional genetics.Nat Methods. 2012 Jan;9(1):14-5. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1843. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 22312629 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alber F, Dokudovskaya S, Veenhoff LM, Zhang W, Kipper J, Devos D, Suprapto A, Karni-Schmidt O, Williams R, Chait BT, et al. Determining the architectures of macromolecular assemblies. Nature. 2007;450:683–694. - PubMed
-
- Alley MR, Maddock JR, Shapiro L. Requirement of the carboxyl terminus of a bacterial chemoreceptor for its targeted proteolysis. Science. 1993;259:1754–1757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

