Vascular inflammation and repair: implications for re-endothelialization, restenosis, and stent thrombosis
- PMID: 22017929
- PMCID: PMC3341937
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcin.2011.05.025
Vascular inflammation and repair: implications for re-endothelialization, restenosis, and stent thrombosis
Abstract
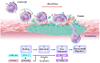
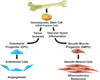
The cellular and molecular processes that control vascular injury responses after percutaneous coronary intervention involve a complex interplay among vascular cells and progenitor cells that control arterial remodeling, neointimal proliferation, and re-endothelialization. Drug-eluting stents (DES) improve the efficacy of percutaneous coronary intervention by modulating vascular inflammation and preventing neointimal proliferation and restenosis. Although positive effects of DES reduce inflammation and restenosis, negative effects delay re-endothelialization and impair endothelial function. Delayed re-endothelialization and impaired endothelial function are linked to stent thrombosis and adverse clinical outcomes after DES use. Compared with bare-metal stents, DES also differentially modulate mobilization, homing, and differentiation of vascular progenitor cells involved in re-endothelialization and neointimal proliferation. The effects of DES on vascular inflammation and repair directly impact clinical outcomes with these devices and dictate requirements for extended-duration dual antiplatelet therapy.
Copyright © 2011 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no significant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to the writing and revision of the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Hilker M, Buerke M, Guckenbiehl M, Schwertz H, Buhler J, Moersig W, Hake U, Oelert H. Rapamycin reduces neointima formation during vascular injury. Vasa. 2003;32:10–13. - PubMed
-
- Park J, Ha H, Ahn HJ, Kang SW, Kim YS, Seo JY, Kim MS. Sirolimus inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-induced collagen synthesis in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Transplant Proc. 2005;37:3459–3462. - PubMed
-
- Costa MA, Simon DI. Molecular basis of restenosis and drug-eluting stents. Circulation. 2005;111:2257–2273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

