The effects of IQPLUS Focus on cognitive function, mood and endocrine response before and following acute exercise
- PMID: 22017963
- PMCID: PMC3210081
- DOI: 10.1186/1550-2783-8-16
The effects of IQPLUS Focus on cognitive function, mood and endocrine response before and following acute exercise
Abstract
Background: Phosphatidylserine (PS) is a phospholipid found in cell membranes of most animals and plants. PS has been shown to reduce stress and increase performance in runners, cyclists and golfers. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of a PS containing formulation on cognitive function, mood and endocrine response before and after intense resistance exercise.
Methods: 18 lower body, resistance trained, college aged males ingested 14 days of supplement (IQPLUS Focus, providing 400 mg of soy-derived PS) and a Placebo (PL), in a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, cross-over manner. Following 14 days of supplementation, participants performed an acute bout of lower body resistance training. Mood (Profile of Mood States, POMS) and cognitive function (Serial Subtraction Test, SST) were measured prior to, 5 minutes after, and 60 minutes after exercise. Venous blood samples were collected prior to, and 5, 15, 25, 40 and 60 minutes after exercise. Blood samples were analyzed for plasma cortisol and testosterone. Data were analyzed using repeated measures ANOVA.
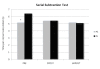
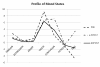
Results: PS supplementation significantly reduced the time needed for a correct calculation on the SST by 20% (reduced by 1.27 s per calculation; PL: 6.4 s, PS: 5.13 s; p = 0.001), and reduced the total amount of errors by 39% (PL: 1.28 + .69, PS: .78 + .27, p = 0.53), and increased the amount of correct calculations by 13% (PL: 22.1 + 2.24, PS: 24.9 + 1.52, p = 0.07) prior to or in response to exercise compared to PL. Following exercise, there was no difference in SST scores between PS and PL. There were no significant changes in regards to mood or endocrine response to exercise as a result of PS supplementation.
Conclusion: PS supplementation significantly increased cognitive function prior to exercise. Improved cognitive function could benefit athletes and non-athletes alike. PS did not appear to affect mood or endocrine response prior to or following resistance exercise.
Figures
References
-
- Crook TH, Tinklenberg J, Yesavage J, Petrie W, Nunzi MG, Massari DC. Effects of phosphatidylserine in age-associated memory impairment. Neurol. 1991;41(5):644–649. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
