How inhibition shapes cortical activity
- PMID: 22017986
- PMCID: PMC3236361
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.027
How inhibition shapes cortical activity
Abstract
Cortical processing reflects the interplay of synaptic excitation and synaptic inhibition. Rapidly accumulating evidence is highlighting the crucial role of inhibition in shaping spontaneous and sensory-evoked cortical activity and thus underscores how a better knowledge of inhibitory circuits is necessary for our understanding of cortical function. We discuss current views of how inhibition regulates the function of cortical neurons and point to a number of important open questions.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

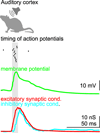
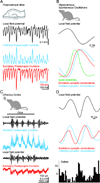
References
-
- Ali AB, Bannister AP, Thomson AM. IPSPs elicited in CA1 pyramidal cells by putative basket cells in slices of adult rat hippocampus. The European journal of neuroscience. 1999;11:1741–1753. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JS, Carandini M, Ferster D. Orientation tuning of input conductance, excitation, and inhibition in cat primary visual cortex. Journal of neurophysiology. 2000;84:909–926. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

