Normal and malignant megakaryopoiesis
- PMID: 22018018
- PMCID: PMC4869998
- DOI: 10.1017/S1462399411002043
Normal and malignant megakaryopoiesis
Abstract
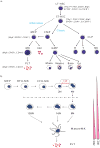
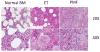
Megakaryopoiesis is the process by which bone marrow progenitor cells develop into mature megakaryocytes (MKs), which in turn produce platelets required for normal haemostasis. Over the past decade, molecular mechanisms that contribute to MK development and differentiation have begun to be elucidated. In this review, we provide an overview of megakaryopoiesis and summarise the latest developments in this field. Specially, we focus on polyploidisation, a unique form of the cell cycle that allows MKs to increase their DNA content, and the genes that regulate this process. In addition, because MKs have an important role in the pathogenesis of acute megakaryocytic leukaemia and a subset of myeloproliferative neoplasms, including essential thrombocythemia and primary myelofibrosis, we discuss the biology and genetics of these disorders. We anticipate that an increased understanding of normal MK differentiation will provide new insights into novel therapeutic approaches that will directly benefit patients.
Figures
References
-
- Lichtman MA, et al. Williams manual of hematology. 8. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2011.
-
- Kanz L, et al. Identification of human megakaryocytes derived from pure megakaryocytic colonies (CFU-M), megakaryocytic-erythroid colonies (CFU-M/E), and mixed hemopoietic colonies (CFU-GEMM) by antibodies against platelet associated antigens. Blut. 1982;45(4):267–274. - PubMed
-
- Nakahata T, Gross AJ, Ogawa M. A stochastic model of self-renewal and commitment to differentiation of the primitive hemopoietic stem cells in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1982;113(3):455–458. - PubMed
-
- Akashi K, et al. A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature. 2000;404(6774):193–197. - PubMed
-
- Reya T, et al. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414(6859):105–111. - PubMed
Further reading, resources and contacts
-
- Tefferi A, Vainchenker W. Myeloproliferative neoplasms: molecular pathophysiology, essential clinical understanding, and treatment strategies. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(5):573–582. Provides a state of the art review of MPNs. - PubMed
-
- Pardanani A, et al. JAK inhibitor therapy for myelofibrosis: critical assessment of value and limitations. Leukemia. 2011;25(2):218–225. Highlights the clinical data for the TargeGen JAK inhibitor. - PubMed
-
- Chagraoui H, et al. SCL-mediated regulation of the cell-cycle regulator p21 is critical for murine megakaryopoiesis. Blood. 2011;118(3):723–735. Demonstrates the essential role of SCL in MKs and identifies p21 as a key target gene. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

