Child maltreatment and allostatic load: consequences for physical and mental health in children from low-income families
- PMID: 22018084
- PMCID: PMC3513367
- DOI: 10.1017/S0954579411000587
Child maltreatment and allostatic load: consequences for physical and mental health in children from low-income families
Abstract
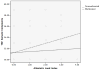
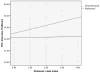
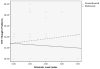
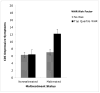
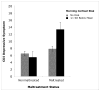
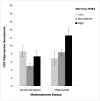
Child maltreatment and biomarkers of allostatic load were investigated in relation to child health problems and psychological symptomatology. Participants attended a summer research day camp and included 137 maltreated and 110 nonmaltreated low-income children, who were aged 8 to 10 years (M = 9.42) and racially and ethnically diverse; 52% were male. Measurements obtained included salivary cortisol and dehydroepiandosterone, body mass index, waist-hip ratio, and blood pressure; these indicators provided a composite index of allostatic load. Child self-report and camp adult-rater reports of child symptomatology were obtained; mothers provided information on health problems. The results indicated that higher allostatic load and child maltreatment status independently predicted poorer health outcomes and greater behavior problems. Moderation effects indicated that allostatic load was related to somatic complaints, attention problems, and thought problems only among maltreated children. Risks associated with high waist-hip ratio, low morning cortisol, and high morning dehydroepiandosterone also were related to depressive symptoms only for maltreated children. The results support an allostatic load conceptualization of the impact of high environmental stress and child abuse and neglect on child health and behavioral outcomes and have important implications for long-term physical and mental health.
Figures
References
-
- Achenbach T. Manual for the Teacher Report Form and 1991 profile. Burlington: Department of Psychiatry, University of Vermont; 1991.
-
- Barnett D, Manly JT, Cicchetti D. Defining child maltreatment: the interface between policy and research. In: Cicchetti D, Toth SL, editors. Child abuse, child development, and social policy. Norwood, NJ: Abex; 1993. pp. 7–73.
-
- Bolger KE, Patterson CJ, Kupersmidt JB. Peer relationships and self-esteem among children who have been maltreated. Child Development. 1998;69:1171–1197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

