Eating for two: how metabolism establishes interspecies interactions in the gut
- PMID: 22018234
- PMCID: PMC3225337
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.10.002
Eating for two: how metabolism establishes interspecies interactions in the gut
Abstract
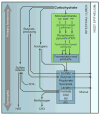
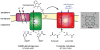
In bacterial communities, "tight economic times" are the norm. Of the many challenges bacteria face in making a living, perhaps none are more important than generating energy, maintaining redox balance, and acquiring carbon and nitrogen to synthesize primary metabolites. The ability of bacteria to meet these challenges depends heavily on the rest of their community. Indeed, the most fundamental way in which bacteria communicate is by importing the substrates for metabolism and exporting metabolic end products. As an illustration of this principle, we will travel down a carbohydrate catabolic pathway common to many species of Bacteroides, highlighting the interspecies interactions established (often inevitably) at its key steps. We also discuss the metabolic considerations in maintaining the stability of host-associated microbial communities.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Alvarez-Acosta T, Leon C, Acosta-Gonzalez S, Parra-Soto H, Cluet-Rodriguez I, Rossell MR, Colina-Chourio JA. Beneficial role of green plantain [Musa paradisiaca] in the management of persistent diarrhea: a prospective randomized trial. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. 2009;28:169–176. - PubMed
-
- Barker HA. Amino acid degradation by anaerobic bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:23–40. - PubMed
-
- Bassler BL, Losick R. Bacterially speaking. Cell. 2006;125:237–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

