Effects of inhibitory amino acids on expression of GABAA Rα and glycine Rα1 in hypoxic rat cortical neurons during development
- PMID: 22018691
- PMCID: PMC3297671
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.09.045
Effects of inhibitory amino acids on expression of GABAA Rα and glycine Rα1 in hypoxic rat cortical neurons during development
Abstract
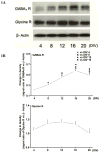
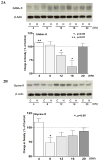
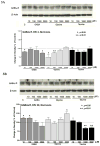
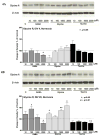
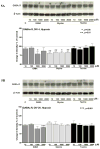
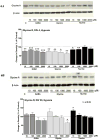
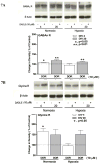
Recent studies suggest that GABA and glycine are protective to mature but toxic to immature cortical neurons during prolonged hypoxia. Since the action of these inhibitory amino acids is mediated by GABA and glycine receptors, the expression of these receptors is a critical factor in determining neuronal response to GABA(A) and glycine in hypoxia. Therefore, we asked whether in rat cortical neurons, 1) hypoxia alters the expression of the GABA and glycine receptors; 2) inhibitory amino acids change the course of GABA and glycine receptor expression; and 3) there are any differences between the immature and mature neurons. In cultured rat cortical neurons from day 4 (four days in vitro or DIV 4) to day 20 (DIV 20), we observed that 1) GABA(A)Rα and GlyRα1 underwent differential changes in expression during the development in vitro; 2) hypoxia for 3 days decreased GABA(A)Rα and GlyRα1 density in the neurons in-between DIV 4 and DIV 20, but did not induce a major change in immature (DIV 4) and mature (DIV 20) neurons; 3) during normoxia GABA, glycine and taurine decreased GABA(A)Rα and GlyRα1 density in the immature neurons, but had a tendency to increase the density in the mature neurons, except for taurine; 4) under hypoxia, all these amino acids decreased GABA(A)Rα and GlyRα1 density in most groups of the immature neurons with a slight effect on the mature neurons; and 5) δ-opioid receptor activation with DADLE increased GABA(A)Rα and GlyRα1 density in both the immature and mature neurons under normoxia and in the mature neurons under hypoxic condition. These data suggest that inhibitory amino acids differentially regulate the expression of GABA(A) and glycine receptors in rat cortical neurons under normoxic and hypoxic conditions with major differences between the immature and mature neurons.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Banasiak KJ, Xia Y, Haddad GG. Mechanisms underlying hypoxia-induced neuronal apoptosis. Prog Neurobiol. 2000;62:215–249. - PubMed
-
- Bekar LK, Jabs R, Walz W. GABAA receptor agonists modulate K+ currents in adult hippocampal glial cells in situ. Glia. 1999;26:129–138. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Excitatory actions of gaba during development: the nature of the nurture. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:728–739. - PubMed
-
- Betz H, Kuhse J, Schmieden V, Laube B, Kirsch J, Harvey RJ. Structure and functions of inhibitory and excitatory glycine receptors. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1999;868:667–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

