Tolerogen-induced interferon-producing killer dendritic cells (IKDCs) protect against EAE
- PMID: 22018711
- PMCID: PMC3237120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.09.005
Tolerogen-induced interferon-producing killer dendritic cells (IKDCs) protect against EAE
Abstract
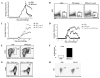
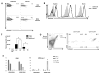
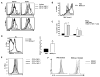
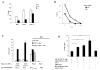
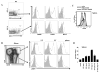
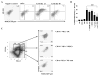
Natural killer (NK) cells and dendritic cells (DCs) have been shown to link the innate and adaptive immune systems. Likewise, a new innate cell subset, interferon-producing killer DCs (IKDCs), shares phenotypic and functional characteristics with both DCs and NK cells. Here, we show IKDCs play an essential role in the resolution of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) upon treatment with the tolerizing agent, myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG), genetically fused to reovirus protein σ1 (termed MOG-pσ1). Activated IKDCs were recruited subsequent MOG-pσ1 treatment of EAE, and disease resolution was abated upon NK1.1 cell depletion. These IKDCs were able to kill activated CD4(+) T cells and mature dendritic DCs, thus, contributing to EAE remission. In addition, IKDCs were responsible for MOG-pσ1-mediated MOG-specific regulatory T cell recruitment to the CNS. The IKDCs induced by MOG-pσ1 expressed elevated levels of HVEM for interactions with cognate ligand-positive cells: LIGHT(+) NK and T(eff) cells and BTLA(+) B cells. Further characterization revealed these activated IKDCs being MHC class II(high), and upon their adoptive transfer (CD11c(+)NK1.1(+)MHC class II(high)), IKDCs, but not CD11c(+)NK1.1(+)MHC class II(intermediate/low) (unactivated) cells, conferred protection against EAE. These activated IKDCs showed enhanced CD107a, PD-L1, and granzyme B expression and could present OVA, unlike unactivated IKDCs. Thus, these results demonstrate the interventional potency induced HVEM(+) IKDCs to resolve autoimmune disease.
2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
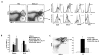
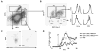
References
-
- Flodstrom-Tullberg M, Bryceson YT, Shi FD, Hoglund P, Ljunggren HG. Natural killer cells in human autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2009;21:634–40. - PubMed
-
- Rabinovich BA, Shannon J, Su RC, Miller RG. Stress renders T cell blasts sensitive to killing by activated syngeneic NK cells. J Immunol. 2000;165:2390–7. - PubMed
-
- Marcenaro E, Della Chiesa M, Bellora F, Parolini S, Millo R, Moretta L, et al. IL-12 or IL-4 prime human NK cells to mediate functionally divergent interactions with dendritic cells or tumors. J Immunol. 2005;174:3992–8. - PubMed
-
- Homann D, Jahreis A, Wolfe T, Hughes A, Coon B, van Stipdonk MJ, et al. CD40L blockade prevents autoimmune diabetes by induction of bitypic NK/DC regulatory cells. Immunity. 2002;16:403–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

