Dynamic association of gammaherpesvirus DNA with core histone during de novo lytic infection of primary cells
- PMID: 22018782
- PMCID: PMC3210866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.09.024
Dynamic association of gammaherpesvirus DNA with core histone during de novo lytic infection of primary cells
Abstract
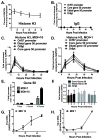
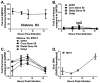
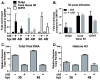
Association of herpesvirus DNA with histones has important implications for lytic and latent infections; thus herpesviruses arbitrate interactions with histones to productively infect host cells. While regulation of alpha and betaherpesvirus chromatin during lytic infection has been actively investigated, very little is known about interaction of gammaherpesvirus DNA with histones upon de novo lytic infection. Murine gammaherpesvirus-68 (MHV68) is a rodent pathogen that offers a tractable system to study gammaherpesvirus lytic infection in primary cells. In this study we report that MHV68 promoter and orilyt sequences underwent dynamic association with histone H3 during de novo lytic infection of primary macrophages and fibroblasts. Similar to HSV-1, the degree of MHV68 DNA association with histone H3 was dependent on the multiplicity of infection and was further regulated by viral DNA synthesis. Our work sets a precedent for future studies of gammaherpesvirus chromatin during de novo lytic infection.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

