Pharmacophore-based discovery of FXR agonists. Part I: Model development and experimental validation
- PMID: 22018919
- PMCID: PMC3254253
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.09.056
Pharmacophore-based discovery of FXR agonists. Part I: Model development and experimental validation
Abstract
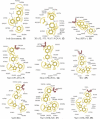
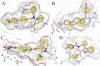
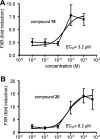
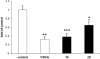
The farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is involved in glucose and lipid metabolism regulation, which makes it an attractive target for the metabolic syndrome, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, and type 2 diabetes. In order to find novel FXR agonists, a structure-based pharmacophore model collection was developed and theoretically evaluated against virtual databases including the ChEMBL database. The most suitable models were used to screen the National Cancer Institute (NCI) database. Biological evaluation of virtual hits led to the discovery of a novel FXR agonist with a piperazine scaffold (compound 19) that shows comparable activity as the endogenous FXR agonist chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA, compound 2).
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Pharmacophore-based discovery of FXR-agonists. Part II: identification of bioactive triterpenes from Ganoderma lucidum.Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Nov 15;19(22):6779-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.09.039. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Bioorg Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 22014750 Free PMC article.
-
Design and identification of a new farnesoid X receptor (FXR) partial agonist by computational structure-activity relationship analysis: Ligand-induced H8 helix fluctuation in the ligand-binding domain of FXR may lead to partial agonism.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021 Jun 1;41:128026. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128026. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 33839252
-
Discovery of new non-steroidal farnesoid X receptor modulators through 3D shape similarity search and structure-based virtual screening.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2015 Apr;85(4):481-7. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.12432. Epub 2014 Oct 10. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2015. PMID: 25228339
-
Farnesoid X receptor: from medicinal chemistry to clinical applications.Future Med Chem. 2012 May;4(7):877-91. doi: 10.4155/fmc.12.41. Future Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22571613 Review.
-
Progress and challenges of selective Farnesoid X Receptor modulation.Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Nov;191:162-177. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.06.009. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29933033 Review.
Cited by
-
Cheminformatics in Natural Product-based Drug Discovery.Mol Inform. 2020 Dec;39(12):e2000171. doi: 10.1002/minf.202000171. Epub 2020 Sep 6. Mol Inform. 2020. PMID: 32725781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of in silico studies dedicated to the nuclear receptor family: Therapeutic prospects and toxicological concerns.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 13;13:986016. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.986016. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36176461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of novel, non-acidic mPGES-1 inhibitors by virtual screening with a multistep protocol.Bioorg Med Chem. 2015 Aug 1;23(15):4839-4845. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.05.045. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26088337 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacophore-based discovery of FXR-agonists. Part II: identification of bioactive triterpenes from Ganoderma lucidum.Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Nov 15;19(22):6779-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.09.039. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Bioorg Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 22014750 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of receptor-based pharmacophore modeling & QM techniques for identification of human chymase inhibitors.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 26;8(4):e63030. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063030. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pellicciari R., Costantino G., Fiorucci S. J. Med. Chem. 2005;48:5383. - PubMed
-
- Chen X., Lin Y., Gilson M.K. J. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2001;4:719. - PubMed
-
- Goodwin B., Jones S.A., Price R.R., Watson M.A., McKee D.D., Moore L.B., Galardi C., Wilson J.G., Lewis M.C., Roth M.E., Maloney P.R., Willson T.M., Kliewer S.A. Mol. Cell. 2000;6:517. - PubMed
-
- Makishima M., Okamoto A.Y., Repa J.J., Tu H., Learned R.M., Luk A., Hull M.V., Lustig K.D., Mangelsdorf D.J., Shan B. Science (New York, NY) 1999;284:1362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

