A46, a benzothiophene-derived compound, suppresses Jak2-mediated pathologic cell growth
- PMID: 22019628
- PMCID: PMC3237899
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2011.10.003
A46, a benzothiophene-derived compound, suppresses Jak2-mediated pathologic cell growth
Abstract
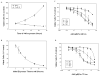
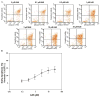
Hyperkinetic Jak2 tyrosine kinase signaling has been implicated in several hematological disorders, including myeloproliferative neoplasms. Effective Jak2 inhibitors can have significant therapeutic potential. Here, using structure-based virtual screening, we identified a benzothiophene-derived Jak2 inhibitor named A46. We hypothesized that this compound would inhibit Jak2-V617F-mediated pathologic cell growth. To test this, A46 was analyzed for its ability to inhibit recombinant Jak2 protein catalysis; suppress Jak2-mediated pathogenic cell growth in vitro; inhibit the aberrant ex vivo growth of Jak2-V617F-expressing primary human bone marrow cells; and inhibit Jak2-mediated pathogenesis in vivo. To this end, we found that A46 selectively inhibited Jak2-V617F protein when compared to wild-type Jak2 protein. The drug also selectively inhibited the proliferation of Jak2-V617F-expressing cells in both a time- and dose-dependent manner, and this correlated with decreased Jak2 and signal transducers and activators of transcription 5 phosphorylation within treated cells. The Jak2-V617F cell growth inhibition correlated with an induction of cell cycle arrest and promotion of apoptosis. A46 also inhibited the pathologic growth of primary Jak2-V617F-expressing bone marrow cells ex vivo. Lastly, using a mouse model of Jak2-V617F-mediated myeloproliferative neoplasia. A46 significantly reduced the splenomegaly and megakaryocytic hyperplasia in the spleens of treated mice and the levels of interleukin-6 in the plasma. Collectively, our data demonstrate that the benzothiophene-based compound, A46, suppresses Jak2-mediated pathogenesis, thereby making it a potential candidate drug against Jak2-mediated disorders.
Copyright © 2012 ISEH - Society for Hematology and Stem Cells. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
The Jak2 inhibitor, G6, alleviates Jak2-V617F-mediated myeloproliferative neoplasia by providing significant therapeutic efficacy to the bone marrow.Neoplasia. 2011 Nov;13(11):1058-68. doi: 10.1593/neo.111112. Neoplasia. 2011. PMID: 22131881 Free PMC article.
-
The stilbenoid tyrosine kinase inhibitor, G6, suppresses Jak2-V617F-mediated human pathological cell growth in vitro and in vivo.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 11;286(6):4280-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.200774. Epub 2010 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21127060 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function correlation of G6, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Jak2: indispensability of the stilbenoid core.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 8;285(41):31399-407. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.168211. Epub 2010 Jul 28. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20667821 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) in myeloproliferative neoplasms: therapeutic implications.Leuk Res. 2013 Apr;37(4):465-72. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2012.12.006. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Leuk Res. 2013. PMID: 23313046 Review.
-
[Analysis of oncogenic signaling pathway induced by a myeloproliferative neoplasm-associated Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) V617F mutant].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012;132(11):1267-72. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.12-00225. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 23123718 Review. Japanese.
References
-
- Parganas E, Wang D, Stravopodis D, et al. Jak2 is essential for signaling through a variety of cytokine receptors. Cell. 1998;93:385–395. - PubMed
-
- Neubauer H, Cumano A, Muller M, Wu H, Huffstadt U, Pfeffer K. Jak2 deficiency defines an essential developmental checkpoint in definitive hematopoiesis. Cell. 1998;93:397–409. - PubMed
-
- Peeters P, Raynaud SD, Cools J, et al. Fusion of TEL, the ETS-variant gene 6 (ETV6), to the receptor-associated kinase JAK2 as a result of t(9;12) in a lymphoid and t(9;15;12) in a myeloid leukemia. Blood. 1997;90:2535–2540. - PubMed
-
- Griesinger F, Hennig H, Hillmer F, et al. A BCR-JAK2 fusion gene as the result of a t(9;22)(p24;q11.2) translocation in a patient with a clinically typical chronic myeloid leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2005;44:329–333. - PubMed
-
- Lacronique V, Boureux A, Valle VD, et al. A TEL-JAK2 fusion protein with constitutive kinase activity in human leukemia. Science. 1997;278:1309–1312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

