Brain uptake of the drug of abuse γ-hydroxybutyric acid in rats
- PMID: 22019629
- PMCID: PMC3250048
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.111.041749
Brain uptake of the drug of abuse γ-hydroxybutyric acid in rats
Abstract
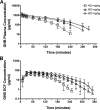
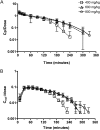
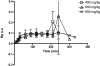
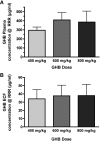
γ-Hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) is an endogenous compound and a substrate for the ubiquitous monocarboxylate transporter (MCT) family. GHB is also a drug of abuse due to its sedative/hypnotic and euphoric effects, with overdoses resulting in toxicity and death. The goal of this study was to characterize the distribution of GHB into the brain using in vivo microdialysis and in vitro uptake studies and to determine concentration-effect relationships for GHB in a rat animal model. GHB was administered to rats (400, 600, and 800 mg/kg i.v.), and blood, dialysate, and urine were collected for 6 h post-GHB administration. The GHB plasma and extracellular fluid (ECF) concentration-time profiles revealed that GHB concentrations in ECF closely followed plasma GHB concentrations. Sleep time increased in a dose-dependent manner (91 ± 18, 134 ± 11, and 168 ± 13 min, for GHB 400, 600, and 800 mg/kg, respectively). GHB partitioning into brain ECF was not significantly different at 400, 600, and 800 mg/kg. GHB uptake in rat and human brain endothelial cells exhibited concentration dependence. The concentration-dependent uptake of GHB at pH 7.4 was best-fit to a single-transporter model [K(m) = 18.1 mM (human), 23.3 mM (rat), V(max) = 248 and 258 pmol · mg(-1) · min(-1) for human and rat, respectively]. These findings indicate that although GHB distribution into the brain is mediated via MCT transporters, it is not capacity-limited over the range of doses studied in this investigation.
Figures


References
-
- Arena C, Fung HL. (1980) Absorption of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate and its prodrug gamma-butyrolactone: relationship between in vitro transport and in vivo absorption. J Pharm Sci 69:356–358 - PubMed
-
- Benavides J, Rumigny JF, Bourguignon JJ, Wermuth CG, Mandel P, Maitre M. (1982) A high-affinity, Na+-dependent uptake system for gamma-hydroxybutyrate in membrane vesicles prepared from rat brain. J Neurochem 38:1570–1575 - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya I, Boje KM. (2004) GHB (gamma-hydroxybutyrate) carrier-mediated transport across the blood-brain barrier. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 311:92–98 - PubMed
-
- Bouw MR, Hammarlund-Udenaes M. (1998) Methodological aspects of the use of a calibrator in in vivo microdialysis-further development of the retrodialysis method. Pharm Res 15:1673–1679 - PubMed
-
- Bowery NG, Hudson AL, Price GW. (1987) GABAA and GABAB receptor site distribution in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 20:365–383 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

