Both negative and positive G1 cell cycle regulators undergo proteasome-dependent degradation during sucrose starvation in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 22019639
- PMCID: PMC3258074
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.6.9.16877
Both negative and positive G1 cell cycle regulators undergo proteasome-dependent degradation during sucrose starvation in Arabidopsis
Abstract
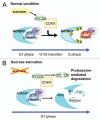
The proteasome pathway regulates many aspects of biological processes in plants, such as plant hormone signaling, light responses, the circadian clock and regulation of cell division. Key cell-cycle regulatory proteins including B-type cyclins, Cdc6, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors and E2Fc undergo proteasome-dependent degradation. We used the proteasome inhibitor MG132 to show that proteolysis of Arabidopsis RETINOBLASTOMA-RELATED 1 (AtRBR1) and three E2Fs is mediated by the proteasome pathway during sucrose starvation in Arabidopsis suspension MM2d cells. We found previously that estrogen-inducible RNAi-mediated downregulation of AtRBR1 leads to a higher frequency of arrest in G2 phase, instead of G1-phase arrest in the uninduced control, after sucrose starvation. Degradation of not only negative (AtRBR1 and E2Fc) but also positive (E2Fa and E2Fb) cell cycle regulators after sucrose starvation may be required for arrest in G1 phase, when cells integrate a variety of nutritional, hormonal and developmental signals to decide whether or not to commit to entry into the cell cycle.
Figures
Comment on
-
Arabidopsis G1 cell cycle proteins undergo proteasome-dependent degradation during sucrose starvation.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2011 Jun;49(6):687-91. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2011.03.001. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21444209
References
-
- Gutierrez C. Coupling cell proliferation and development in plants. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:535–541. - PubMed
-
- Gupta AK, Kaur N. Sugar signaling and gene expression in relation to carbohydrate metabolism under abiotic stresses in plants. J Biosci. 2005;30:761–776. - PubMed
-
- Pines J. Four-dimensional control of the cell cycle. Nat Cell Biol. 1999;1:73–79. - PubMed
-
- Joubes J, Chevalier C, Dudits D, Heberle-Bors E, Inze D, Umeda M, Renaudi JP. CDK-related protein kinases in plants. Plant Mol Biol. 2000;43:607–620. - PubMed
-
- Inze D, De Veylder L. Cell cycle regulation in plant development. Ann Rev Genet. 2006;40:77–105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
