Neutrophil-cytokine interactions in a rat model of sulindac-induced idiosyncratic liver injury
- PMID: 22019926
- PMCID: PMC3226905
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2011.10.005
Neutrophil-cytokine interactions in a rat model of sulindac-induced idiosyncratic liver injury
Abstract
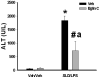
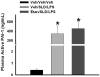
Previous studies indicated that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) interacts with the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug sulindac (SLD) to produce liver injury in rats. In the present study, the mechanism of SLD/LPS-induced liver injury was further investigated. Accumulation of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) in the liver was greater in SLD/LPS-cotreated rats compared to those treated with SLD or LPS alone. In addition, PMN activation occurred specifically in livers of rats cotreated with SLD/LPS. The hypothesis that PMNs and proteases released from them play critical roles in the hepatotoxicity was tested. SLD/LPS-induced liver injury was attenuated by prior depletion of PMNs or by treatment with the PMN protease inhibitor, eglin C. Previous studies suggested that tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF) and the hemostatic system play critical roles in the pathogenesis of liver injury induced by SLD/LPS. TNF and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) can contribute to hepatotoxicity by affecting PMN activation and fibrin deposition. Therefore, the role of TNF and PAI-1 in PMN activation and fibrin deposition in the SLD/LPS-induced liver injury model was tested. Neutralization of TNF or inhibition of PAI-1 attenuated PMN activation. TNF had no effect on PAI-1 production or fibrin deposition. In contrast, PAI-1 contributed to fibrin deposition in livers of rats treated with SLD/LPS. In summary, PMNs, TNF and PAI-1 contribute to the liver injury induced by SLD/LPS cotreatment. TNF and PAI-1 independently contributed to PMN activation, which is critical to the pathogenesis of liver injury. Moreover, PAI-1 contributed to liver injury by promoting fibrin deposition.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
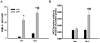
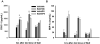

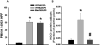




References
-
- Baranes D, Matzner J, Razin E. Thrombin-induced calcium-independent degranulation of human neutrophils. Inflammation. 1986;10:455–461. - PubMed
-
- Braun NJ, Bodmer JL, Virca GD, Metz-Virca G, Maschler R, Bieth JG, Schnebli HP. Kinetic studies on the interaction of eglin c with human leukocyte elastase and cathepsin G. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987;368:299–308. - PubMed
-
- Chosay JG, Essani NA, Dunn CJ, Jaeschke H. Neutrophil margination and extravasation in sinusoids and venules of liver during endotoxin-induced injury. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:G1195–1200. - PubMed
-
- Copple BL, Moulin F, Hanumegowda UM, Ganey PE, Roth RA. Thrombin and protease-activated receptor-1 agonists promote lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatocellular injury in perfused livers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;305:417–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

