Bone marrow and the control of immunity
- PMID: 22020068
- PMCID: PMC3251706
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2011.47
Bone marrow and the control of immunity
Abstract
Bone marrow is thought to be a primary hematopoietic organ. However, accumulated evidences demonstrate that active function and trafficking of immune cells, including regulatory T cells, conventional T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, natural killer T (NKT) cells, neutrophils, myeloid-derived suppressor cells and mesenchymal stem cells, are observed in the bone marrow. Furthermore, bone marrow is a predetermined metastatic location for multiple human tumors. In this review, we discuss the immune network in the bone marrow. We suggest that bone marrow is an immune regulatory organ capable of fine tuning immunity and may be a potential therapeutic target for immunotherapy and immune vaccination.
Figures

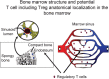

References
-
- Kopp HG, Avecilla ST, Hooper AT, Rafii S. The bone marrow vascular niche: home of HSC differentiation and mobilization. Physiology (Bethesda) 2005;20:349–356. - PubMed
-
- Rafii S, Lyden D. Therapeutic stem and progenitor cell transplantation for organ vascularization and regeneration. Nat Med. 2003;9:702–712. - PubMed
-
- Tripp RA, Topham DJ, Watson SR, Doherty PC. Bone marrow can function as a lymphoid organ during a primary immune response under conditions of disrupted lymphocyte trafficking. J Immunol. 1997;158:3716–3720. - PubMed
-
- Dejbakhsh-Jones S, Jerabek L, Weissman IL, Strober S. Extrathymic maturation of alpha beta T cells from hemopoietic stem cells. J Immunol. 1995;155:3338–3344. - PubMed
-
- Schirrmacher V, Feuerer M, Fournier P, Ahlert T, Umansky V, Beckhove P. T-cell priming in bone marrow: the potential for long-lasting protective anti-tumor immunity. Trends Mol Med. 2003;9:526–534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

