Acquired self-control of insula cortex modulates emotion recognition and brain network connectivity in schizophrenia
- PMID: 22021045
- PMCID: PMC6869886
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21427
Acquired self-control of insula cortex modulates emotion recognition and brain network connectivity in schizophrenia
Abstract
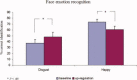
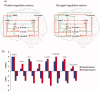
Real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging (rtfMRI) is a novel technique that has allowed subjects to achieve self-regulation of circumscribed brain regions. Despite its anticipated therapeutic benefits, there is no report on successful application of this technique in psychiatric populations. The objectives of the present study were to train schizophrenia patients to achieve volitional control of bilateral anterior insula cortex on multiple days, and to explore the effect of learned self-regulation on face emotion recognition (an extensively studied deficit in schizophrenia) and on brain network connectivity. Nine patients with schizophrenia were trained to regulate the hemodynamic response in bilateral anterior insula with contingent rtfMRI neurofeedback, through a 2-weeks training. At the end of the training stage, patients performed a face emotion recognition task to explore behavioral effects of learned self-regulation. A learning effect in self-regulation was found for bilateral anterior insula, which persisted through the training. Following successful self-regulation, patients recognized disgust faces more accurately and happy faces less accurately. Improvements in disgust recognition were correlated with levels of self-activation of right insula. RtfMRI training led to an increase in the number of the incoming and outgoing effective connections of the anterior insula. This study shows for the first time that patients with schizophrenia can learn volitional brain regulation by rtfMRI feedback training leading to changes in the perception of emotions and modulations of the brain network connectivity. These findings open the door for further studies of rtfMRI in severely ill psychiatric populations, and possible therapeutic applications.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Abler B, Roebroeck A, Goebel R, Hose A, Schonfeldt‐Lecuona C, Hole G, Walter H ( 2006): Investigating directed influences between activated brain areas in a motor‐response task using fMRI. Magn Reson Imaging 24: 181–185. - PubMed
-
- Addington D, Addington J, Schissel B ( 1990): A depression rating scale for schizophrenics. Schizophr Res 3: 247–251. - PubMed
-
- Addington J, Addington D ( 1998): Facial affect recognition and information processing in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Res 32: 171–181. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R ( 2002): Neural systems for recognizing emotion. Current Opin Neurobiol 12: 169–177. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R, Tranel D, Damasio AR ( 2003): Dissociable neural systems for recognizing emotions. Brain Cogn 52: 61–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

