A wide extent of inter-strain diversity in virulent and vaccine strains of alphaherpesviruses
- PMID: 22022263
- PMCID: PMC3192842
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002282
A wide extent of inter-strain diversity in virulent and vaccine strains of alphaherpesviruses
Abstract
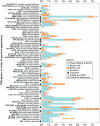
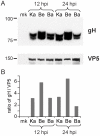
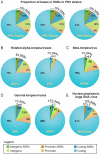
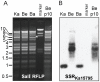
Alphaherpesviruses are widespread in the human population, and include herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) and 2, and varicella zoster virus (VZV). These viral pathogens cause epithelial lesions, and then infect the nervous system to cause lifelong latency, reactivation, and spread. A related veterinary herpesvirus, pseudorabies (PRV), causes similar disease in livestock that result in significant economic losses. Vaccines developed for VZV and PRV serve as useful models for the development of an HSV-1 vaccine. We present full genome sequence comparisons of the PRV vaccine strain Bartha, and two virulent PRV isolates, Kaplan and Becker. These genome sequences were determined by high-throughput sequencing and assembly, and present new insights into the attenuation of a mammalian alphaherpesvirus vaccine strain. We find many previously unknown coding differences between PRV Bartha and the virulent strains, including changes to the fusion proteins gH and gB, and over forty other viral proteins. Inter-strain variation in PRV protein sequences is much closer to levels previously observed for HSV-1 than for the highly stable VZV proteome. Almost 20% of the PRV genome contains tandem short sequence repeats (SSRs), a class of nucleic acids motifs whose length-variation has been associated with changes in DNA binding site efficiency, transcriptional regulation, and protein interactions. We find SSRs throughout the herpesvirus family, and provide the first global characterization of SSRs in viruses, both within and between strains. We find SSR length variation between different isolates of PRV and HSV-1, which may provide a new mechanism for phenotypic variation between strains. Finally, we detected a small number of polymorphic bases within each plaque-purified PRV strain, and we characterize the effect of passage and plaque-purification on these polymorphisms. These data add to growing evidence that even plaque-purified stocks of stable DNA viruses exhibit limited sequence heterogeneity, which likely seeds future strain evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Roizman B, Pellett PE. The family Herpesviridae: A brief introduction. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Fields Virology 4 ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. pp. 2381–2397.
-
- Steiner I, Kennedy PG, Pachner AR. The neurotropic herpes viruses: herpes simplex and varicella-zoster. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:1015–1028. - PubMed
-
- Mettenleiter TC, Keil GM, Fuchs W. Molecular Biology of Animal Herpesviruses. In: Mettenleiter TC, Sobrino F, editors. Animal viruses: molecular biology. xii. Norfolk, UK: Caister Academic Press; 2008. p. 531.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

