Structural basis for specific binding of human MPP8 chromodomain to histone H3 methylated at lysine 9
- PMID: 22022377
- PMCID: PMC3192050
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025104
Structural basis for specific binding of human MPP8 chromodomain to histone H3 methylated at lysine 9
Abstract
Background: M-phase phosphoprotein 8 (MPP8) was initially identified to be a component of the RanBPM-containing large protein complex, and has recently been shown to bind to methylated H3K9 both in vivo and in vitro. MPP8 binding to methylated H3K9 is suggested to recruit the H3K9 methyltransferases GLP and ESET, and DNA methyltransferase 3A to the promoter of the E-cadherin gene, mediating the E-cadherin gene silencing and promote tumor cell motility and invasion. MPP8 contains a chromodomain in its N-terminus, which is used to bind the methylated H3K9.
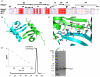
Methodology/principal findings: Here, we reported the crystal structures of human MPP8 chromodomain alone and in complex with the trimethylated histone H3K9 peptide (residue 1-15). The complex structure unveils that the human MPP8 chromodomain binds methylated H3K9 through a conserved recognition mechanism, which was also observed in Drosophila HP1, a chromodomain containing protein that binds to methylated H3K9 as well. The structure also reveals that the human MPP8 chromodomain forms homodimer, which is mediated via an unexpected domain swapping interaction through two β strands from the two protomer subunits.
Conclusions/significance: Our findings reveal the molecular mechanism of selective binding of human MPP8 chromodomain to methylated histone H3K9. The observation of human MPP8 chromodomain in both solution and crystal lattice may provide clues to study MPP8-mediated gene regulation furthermore.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tri-methylation of ATF7IP by G9a/GLP recruits the chromodomain protein MPP8.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018 Oct 4;11(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13072-018-0231-z. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018. PMID: 30286792 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the recognition of methylated histone H3 by the Arabidopsis LHP1 chromodomain.J Biol Chem. 2022 Mar;298(3):101623. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101623. Epub 2022 Jan 21. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35074427 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of HP1 chromodomain bound to a lysine 9-methylated histone H3 tail.Science. 2002 Mar 15;295(5562):2080-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1069473. Epub 2002 Feb 21. Science. 2002. PMID: 11859155
-
Effector proteins for methylated histones: an expanding family.Cell Cycle. 2005 Jul;4(7):919-26. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.7.1824. Epub 2005 Jul 5. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 15970672 Review.
-
Epigenetic virtues of chromodomains.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011 Dec;46(6):507-26. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2011.619164. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 22023491 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Keep quiet: the HUSH complex in transcriptional silencing and disease.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Jan;31(1):11-22. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01173-7. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38216658 Review.
-
TNRC18 engages H3K9me3 to mediate silencing of endogenous retrotransposons.Nature. 2023 Nov;623(7987):633-642. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06688-z. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37938770 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of retinal development and disease.J Ocul Biol Dis Infor. 2011 Sep;4(3):121-36. doi: 10.1007/s12177-012-9083-0. Epub 2012 Mar 29. J Ocul Biol Dis Infor. 2011. PMID: 23538488 Free PMC article.
-
Modified Histone Peptides Linked to Magnetic Beads Reduce Binding Specificity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 1;23(3):1691. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031691. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163614 Free PMC article.
-
Application of histone modification-specific interaction domains as an alternative to antibodies.Genome Res. 2014 Nov;24(11):1842-53. doi: 10.1101/gr.170985.113. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 25301795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vaquero A, Loyola A, Reinberg D. The constantly changing face of chromatin. Sci Aging Knowledge Environ. 2003;2003:RE4. - PubMed
-
- Hake SB, Xiao A, Allis CD. Linking the epigenetic ‘language’ of covalent histone modifications to cancer. Br J Cancer. 2007;96(Suppl):R31–39. - PubMed
-
- Strahl BD, Allis CD. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature. 2000;403:41–45. - PubMed
-
- Adams-Cioaba MA, Min J. Structure and function of histone methylation binding proteins. Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;87:93–105. - PubMed
-
- Sims RJ, Nishioka K, Reinberg D. Histone lysine methylation: a signature for chromatin function. Trends Genet. 2003;19:629–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

