The molecular signature underlying the thymic migration and maturation of TCRαβ+ CD4+ CD8 thymocytes
- PMID: 22022412
- PMCID: PMC3192722
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025567
The molecular signature underlying the thymic migration and maturation of TCRαβ+ CD4+ CD8 thymocytes
Abstract
Background: After positive selection, the newly generated single positive (SP) thymocytes migrate to the thymic medulla, where they undergo negative selection to eliminate autoreactive T cells and functional maturation to acquire immune competence and egress capability.
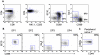
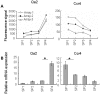
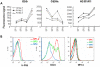
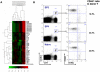
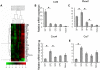
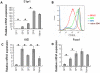
Methodology/principal findings: To elucidate the genetic program underlying this process, we analyzed changes in gene expression in four subsets of mouse TCRαβ(+)CD4(+)CD8(-) thymocytes (SP1 to SP4) representative of sequential stages in a previously defined differentiation program. A genetic signature of the migration of thymocytes was thus revealed. CCR7 and PlexinD1 are believed to be important for the medullary positioning of SP thymocytes. Intriguingly, their expression remains at low levels in the newly generated thymocytes, suggesting that the cortex-medulla migration may not occur until the SP2 stage. SP2 and SP3 cells gradually up-regulate transcripts involved in T cell functions and the Foxo1-KLF2-S1P(1) axis, but a number of immune function-associated genes are not highly expressed until cells reach the SP4 stage. Consistent with their critical role in thymic emigration, the expression of S1P(1) and CD62L are much enhanced in SP4 cells.
Conclusions: These results support at the molecular level that single positive thymocytes undergo a differentiation program and further demonstrate that SP4 is the stage at which thymocytes acquire the immunocompetence and the capability of emigration from the thymus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

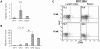
Similar articles
-
Redox balance of mouse medullary CD4 single-positive thymocytes.Immunol Cell Biol. 2013 Nov-Dec;91(10):634-41. doi: 10.1038/icb.2013.57. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24100390
-
Characterization of the in vivo dynamics of medullary CD4+CD8- thymocyte development.J Immunol. 2008 Feb 15;180(4):2256-63. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.4.2256. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18250433
-
Human CD4 expression at the late single-positive stage of thymic development supports T cell maturation and peripheral export in CD4-deficient mice.J Immunol. 2002 Oct 15;169(8):4347-53. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.8.4347. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12370367
-
The biology of recent thymic emigrants.Annu Rev Immunol. 2013;31:31-50. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-100010. Epub 2012 Nov 1. Annu Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23121398 Review.
-
Thymocyte migration and emigration.Immunol Lett. 2024 Jun;267:106861. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2024.106861. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Immunol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38697225 Review.
Cited by
-
Maturation and emigration of single-positive thymocytes.Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:282870. doi: 10.1155/2013/282870. Epub 2013 Sep 29. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24187562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymus medulla fosters generation of natural Treg cells, invariant γδ T cells, and invariant NKT cells: what we learn from intrathymic migration.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Mar;45(3):652-60. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445108. Epub 2015 Feb 13. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25615828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homeostatic properties and phenotypic maturation of murine CD4+ pre-thymic emigrants in the thymus.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056378. Epub 2013 Feb 11. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23409179 Free PMC article.
-
Thymic Egress Is Regulated by T Cell-Derived LTβR Signal and via Distinct Thymic Portal Endothelial Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 1;12:707404. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.707404. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34276703 Free PMC article.
-
The thymus medulla and its control of αβT cell development.Semin Immunopathol. 2021 Feb;43(1):15-27. doi: 10.1007/s00281-020-00830-z. Epub 2020 Dec 11. Semin Immunopathol. 2021. PMID: 33306154 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rodewald HR. Thymus organogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:355–388. - PubMed
-
- Takahama Y. Journey through the thymus: stromal guides for T-cell development and selection. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:127–135. - PubMed
-
- Ramsdell F, Jenkins M, Dinh Q, Fowlkes BJ. The majority of CD4+8- thymocytes are functionally immature. J Immunol. 1991;147:1779–1785. - PubMed
-
- Vicari A, Abehsira-Amar O, Papiernik M, Boyd RL, Tucek CL. MTS-32 monoclonal antibody defines CD4+8- thymocyte subsets that differ in their maturation level, lymphokine secretion, and selection patterns. J Immunol. 1994;152:2207–2213. - PubMed
-
- Lucas B, Vasseur F, Penit C. Production, selection, and maturation of thymocytes with high surface density of TCR. J Immunol. 1994;153:53–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

