Maternal history of reading difficulty is associated with reduced language-related gray matter in beginning readers
- PMID: 22023744
- PMCID: PMC3628690
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.024
Maternal history of reading difficulty is associated with reduced language-related gray matter in beginning readers
Abstract
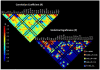
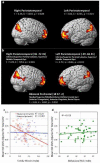
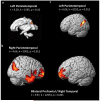
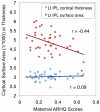
Family history and poor preliteracy skills (referred to here as familial and behavioral risk, respectively) are critical predictors of developmental dyslexia. This study systematically investigated the independent contribution of familial and behavioral risks on brain structures, which had not been explored in past studies. We also examined the differential effects of maternal versus paternal history on brain morphometry, and familial risk dimensionally versus categorically, which were also novel aspects of the study. We assessed 51 children (5 to 6 years of age) with varying degrees of familial and behavioral risks for developmental dyslexia and examined associations with brain morphometry. We found that greater maternal history of reading disability was associated with smaller bilateral prefrontal and parieto-temporal gray, but not white matter volumes. Regressing out behavioral risk, socioeconomic status, and maternal education and other confounds did not change the results. No such relationship was observed for paternal reading history and behavioral risk. Results of cortical surface area and thickness further showed that there was a significant negative relationship between cortical surface area (but not thickness) and greater severity of maternal history, in particular within the left inferior parietal lobule, suggesting prenatal influence of maternal history on children's brain morphometry. The results suggested greater maternal, possibly prenatal, influence on language-related brain structures. These results help to guide future neuroimaging research focusing on environmental and genetic influences and provide new information that may help predict which child will develop dyslexia in the future.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neural correlates of rapid auditory processing are disrupted in children with developmental dyslexia and ameliorated with training: an fMRI study.Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2007;25(3-4):295-310. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17943007
-
Surface area accounts for the relation of gray matter volume to reading-related skills and history of dyslexia.Cereb Cortex. 2010 Nov;20(11):2625-35. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq010. Epub 2010 Feb 12. Cereb Cortex. 2010. PMID: 20154011 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Influences of Language Delay and/or Familial Risk for Dyslexia on Brain Structure in 5-Year-Olds.Cereb Cortex. 2017 Jan 1;27(1):764-776. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhv267. Cereb Cortex. 2017. PMID: 26585334 Free PMC article.
-
Dyslexia: a new synergy between education and cognitive neuroscience.Science. 2009 Jul 17;325(5938):280-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1171999. Science. 2009. PMID: 19608907 Review.
-
Developmental dyslexia: an update on genes, brains, and environments.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2001 Jan;42(1):91-125. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2001. PMID: 11205626 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain and behavioral correlates of insulin resistance in youth with depression and obesity.Horm Behav. 2019 Feb;108:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2018.03.009. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Horm Behav. 2019. PMID: 29596854 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Possible roles for fronto-striatal circuits in reading disorder.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017 Jan;72:243-260. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.10.025. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017. PMID: 27826071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topological properties of large-scale structural brain networks in children with familial risk for reading difficulties.Neuroimage. 2013 May 1;71:260-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.01.013. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Neuroimage. 2013. PMID: 23333415 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Correlates of Oral Word Reading, Silent Reading Comprehension, and Cognitive Subcomponents.Int J Behav Dev. 2018 May;42(3):342-356. doi: 10.1177/0165025417727872. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Int J Behav Dev. 2018. PMID: 29904229 Free PMC article.
-
The cognitive basis of dyslexia in school-aged children: A multiple case study in a transparent orthography.Dev Sci. 2022 Mar;25(2):e13173. doi: 10.1111/desc.13173. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Dev Sci. 2022. PMID: 34448328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alloway TP, Gathercole SE, Willis C, Adams AM. A structural analysis of working memory and related cognitive skills in young children. J Exp Child Psychol. 2004;87:85–106. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage. 2007;38:95–113. - PubMed
-
- Aylward EH, Richards TL, Beringer VW, Nagy WE, Field KM, Grimme AC, Richards AL, Thomson JB, Cramer SC. Instructional treatment associated with changes in brain activation in children with dyslexia. Neurology. 2003;61:212–219. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein MH, Bradley RH, editors. Socioeconomic Status, Parenting, and Child Development. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; Mahwah: 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

