Class III PI-3-kinase activates phospholipase D in an amino acid-sensing mTORC1 pathway
- PMID: 22024166
- PMCID: PMC3206351
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201107033
Class III PI-3-kinase activates phospholipase D in an amino acid-sensing mTORC1 pathway
Abstract
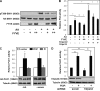
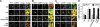
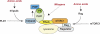
The rapamycin-sensitive mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex, mTORC1, regulates cell growth in response to mitogenic signals and amino acid availability. Phospholipase D (PLD) and its product, phosphatidic acid, have been established as mediators of mitogenic activation of mTORC1. In this study, we identify a novel role for PLD1 in an amino acid-sensing pathway. We find that amino acids activate PLD1 and that PLD1 is indispensable for amino acid activation of mTORC1. Activation of PLD1 by amino acids requires the class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase hVps34, which stimulates PLD1 activity through a functional interaction between phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and the Phox homology (PX) domain of PLD1. Furthermore, amino acids stimulate PLD1 translocation to the lysosomal region where mTORC1 activation occurs in an hVps34-dependent manner, and this translocation is necessary for mTORC1 activation. The PX domain is required for PLD1 translocation, mTORC1 activation, and cell size regulation. Finally, we show that the hVps34-PLD1 pathway acts independently of, and in parallel to, the Rag pathway in regulating amino acid activation of mTORC1.
Figures


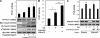




Similar articles
-
Leucyl-tRNA Synthetase Activates Vps34 in Amino Acid-Sensing mTORC1 Signaling.Cell Rep. 2016 Aug 9;16(6):1510-1517. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.07.008. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27477288 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase D mediates nutrient input to mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1).J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 22;286(29):25477-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.249631. Epub 2011 May 28. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21622984 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct amino acid-sensing mTOR pathways regulate skeletal myogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Dec;24(23):3754-63. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-06-0353. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 24068326 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid regulation of TOR complex 1.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Apr;296(4):E592-602. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90645.2008. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 18765678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vps34 and PLD1 take center stage in nutrient signaling: their dual roles in regulating autophagy.Cell Commun Signal. 2015 Nov 21;13:44. doi: 10.1186/s12964-015-0122-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2015. PMID: 26589724 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphatidic acid and lipid-sensing by mTOR.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Jun;24(6):272-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2013.02.003. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23507202 Free PMC article.
-
Class III PI3K Biology.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2022;436:69-93. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-06566-8_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36243840
-
Phosphatidylinositol Kinases and Phosphatases in Entamoeba histolytica.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Jun 6;9:150. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00150. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31245297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of diacylglycerol kinase ζ and phosphatidic acid in the mechanical activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling and skeletal muscle hypertrophy.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 17;289(3):1551-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.531392. Epub 2013 Dec 3. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24302719 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal control of phosphatidic acid signaling with optogenetic, engineered phospholipase Ds.J Cell Biol. 2020 Mar 2;219(3):e201907013. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201907013. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31999306 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

