Novel protein-based pneumococcal vaccines administered with the Th1-promoting adjuvant IC31 induce protective immunity against pneumococcal disease in neonatal mice
- PMID: 22025519
- PMCID: PMC3255653
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.05801-11
Novel protein-based pneumococcal vaccines administered with the Th1-promoting adjuvant IC31 induce protective immunity against pneumococcal disease in neonatal mice
Abstract
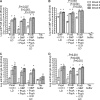
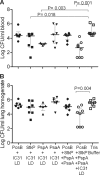
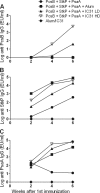
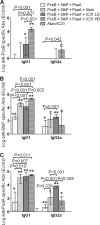
Streptococcus pneumoniae is responsible for many vaccine-preventable deaths, annually causing around 1 million deaths in children younger than 5 years of age. A new generation of pneumococcal vaccines based on conserved proteins is being developed. We evaluated the immunogenicities and protective efficacies of four pneumococcal protein vaccine candidates, PcsB, StkP, PsaA, and PspA, in a neonatal mouse model. Mice were immunized three times and challenged intranasally with virulent pneumococci. All four proteins were immunogenic in neonatal mice, and antibody (Ab) responses were significantly enhanced by the novel adjuvant IC31, which consists of an antibacterial peptide (KLKL5KLK) and a synthetic oligodeoxynucleotide, ODN1a, that signals through Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9). Two single proteins, StkP and PspA, combined with IC31 significantly reduced pneumococcal bacteremia but had no effects on lung infection. Three proteins, PcsB, StkP, and PsaA, were evaluated with alum or IC31. IC31 enhanced Ab responses and avidity to all three proteins, whereas alum enhanced Ab responses and avidity to StkP and PsaA only. Mice receiving the trivalent protein formulation with IC31 had significantly reduced bacteremia and lung infection compared to unvaccinated mice, but the level of protection was dependent on the dose of IC31. When PspA was added to the trivalent protein formulation, the dose of IC31 needed to obtain protective immunity could be reduced. These results demonstrate that a novel pneumococcal protein-based vaccine is immunogenic at an early age of mice and emphasize the benefits of using a combination of conserved proteins and an effective adjuvant to elicit potent protective immunity against invasive pneumococcal disease.
Figures

References
-
- Agger EM, et al. 2006. Protective immunity to tuberculosis with Ag85B-ESAT-6 in a synthetic cationic adjuvant system IC31. Vaccine 24: 5452–5460 - PubMed
-
- Arulanandam BP, Lynch JM, Briles DE, Hollingshead S, Metzger DW. 2001. Intranasal vaccination with pneumococcal surface protein A and interleukin-12 augments antibody-mediated opsonization and protective immunity against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. Infect. Immun. 69: 6718–6724 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Black S, et al. 2000. Efficacy, safety and immunogenicity of heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in children. Northern California Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center Group. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 19: 187–195 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

