Mania-like behavior induced by genetic dysfunction of the neuron-specific Na+,K+-ATPase α3 sodium pump
- PMID: 22025725
- PMCID: PMC3207708
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1108416108
Mania-like behavior induced by genetic dysfunction of the neuron-specific Na+,K+-ATPase α3 sodium pump
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Feb 7;109(6):2174
Abstract
Bipolar disorder is a debilitating psychopathology with unknown etiology. Accumulating evidence suggests the possible involvement of Na(+),K(+)-ATPase dysfunction in the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder. Here we show that Myshkin mice carrying an inactivating mutation in the neuron-specific Na(+),K(+)-ATPase α3 subunit display a behavioral profile remarkably similar to bipolar patients in the manic state. Myshkin mice show increased Ca(2+) signaling in cultured cortical neurons and phospho-activation of extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) and Akt in the hippocampus. The mood-stabilizing drugs lithium and valproic acid, specific ERK inhibitor SL327, rostafuroxin, and transgenic expression of a functional Na(+),K(+)-ATPase α3 protein rescue the mania-like phenotype of Myshkin mice. These findings establish Myshkin mice as a unique model of mania, reveal an important role for Na(+),K(+)-ATPase α3 in the control of mania-like behavior, and identify Na(+),K(+)-ATPase α3, its physiological regulators and downstream signal transduction pathways as putative targets for the design of new antimanic therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

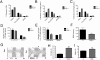
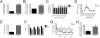

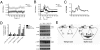
References
-
- Goldstein I, et al. Association between sodium- and potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase alpha isoforms and bipolar disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65:985–991. - PubMed
-
- Dobretsov M, Stimers JR. Neuronal function and alpha3 isoform of the Na/K-ATPase. Front Biosci. 2005;10:2373–2396. - PubMed
-
- Croyle ML, Woo AL, Lingrel JB. Extensive random mutagenesis analysis of the Na+/K+-ATPase alpha subunit identifies known and previously unidentified amino acid residues that alter ouabain sensitivity—Implications for ouabain binding. Eur J Biochem. 1997;248:488–495. - PubMed
-
- Schoner W, Scheiner-Bobis G. Endogenous and exogenous cardiac glycosides and their mechanisms of action. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2007;7:173–189. - PubMed
-
- Urayama O, Sweadner KJ. Ouabain sensitivity of the alpha 3 isozyme of rat Na,K-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988;156:796–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

