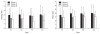The effect of epidural administration of dexamethasone on postoperative pain: a randomized controlled study in radical subtotal gastrectomy
- PMID: 22025946
- PMCID: PMC3198185
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2011.61.3.233
The effect of epidural administration of dexamethasone on postoperative pain: a randomized controlled study in radical subtotal gastrectomy
Abstract
Background: Epidurally administered dexamethasone may reduce the incidence and severity of postoperative pain. We investigated whether postoperative pain could be alleviated by preoperative or postoperative epidural dexamethasone administration in patients undergoing major abdominal surgery.
Methods: Ninety patients (age 30-77 with American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I and II) undergoing radical subtotal gastrectomy were randomly allocated to three groups using computer generated randomization. In all groups, 10 ml of 0.25% ropivacaine was injected epidurally before the start and at the end of the operation. In Group I, a bolus ropivacaine epidural without dexamethasone was administered. In Group II, dexamethasone (5 mg) was added to the ropivacaine bolus epidural before the start of operation. In Group III, the same amount of dexamethasone was given with the ropivacaine epidural at the end of operation. Effort and resting VAS, the use of rescue analgesics and any complications noted during the procedure were evaluated.
Results: VAS and requirements of rescue analgesics were significantly lower in Groups II and III when compared to Group I. There were no difference in the incidence of nausea and vomiting between groups, but an itching sensation was frequent in Group III.
Conclusions: The administration of 5 mg of dexamethasone epidurallly, before or after operation, could reduce the pain and analgesic requirement after radical subtotal gastrectomy.
Keywords: Dexamethasone; Epidural; Gastrectomy.
Figures
References
-
- Abram SE, Marsala M, Yaksh TL. Analgesic and neurotoxic effects of intrathecal corticosteroids in rats. Anesthesiology. 1994;81:1198–1205. - PubMed
-
- Yao XL, Cowan MJ, Gladwin MT, Lawrence MM, Angus CW, Shelhamer JH. Dexamethasone alters arachidonate release from human epithelial cells by induction of p11 protein synthesis and inhibition of phospholipase A2 activity. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:17202–17208. - PubMed
-
- Ebersberger A, Grubb BD, Willingale HL, Gardiner NJ, Nebe J, Schaible HG. The intraspinal release of prostaglandin E2 in a model of acute arthritis is accompanied by an up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in the spinal cord. Neuroscience. 1999;93:775–781. - PubMed
-
- Wang YL, Tan PP, Yang CH, Tsai SC, Chung HS. Epidural dexamethasone reduces the incidence of backache after lumbar epidural anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1997;84:376–378. - PubMed
-
- Thomas S, Beevi S. Epidural dexamethasone reduces postoperative pain and analgesic requirements. Can J Anaesth. 2006;53:899–905. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources