Effects of intraoperative low dose ketamine on remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia in gynecologic surgery with sevoflurane anesthesia
- PMID: 22025947
- PMCID: PMC3198186
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2011.61.3.238
Effects of intraoperative low dose ketamine on remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia in gynecologic surgery with sevoflurane anesthesia
Abstract
Background: Remifentanil is useful during general anesthesia because of its rapid onset and short acting time. However, some studies report that due to opioid-induced hyperalgesia (OIH) and tolerance, remifentanil also increases early postoperative pain. The occurrence of OIH and opioid-induced tolerance is mainly thought to be due to central sensitization by the activation of NMDA receptors. Therefore, we investigated the effects of continuous infusion of ketamine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, on postoperative pain and the quantity of opioids used.
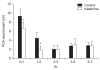
Methods: 40 patients scheduled to undergo laparoscopic gynecologic surgery were randomly allocated into two groups. Anesthesia was equally maintained with sevoflurane and 4 ng/ml of remifentanil in all patients. Ketamine (0.3 mg/kg) was injected and followed with a continuous dosage of 3 µl/kg/min in the ketamine group (n = 20) while the control group was injected and infused with an equal amount of normal saline. We compared postoperative VAS up to 7 hours and morphine demand through PCA.
Results: Postoperative VAS and morphine demand was significantly lower in the ketamine group 2 and 3 hours after surgery, respectively.
Conclusions: When general anesthesia is maintained with sevoflurane and remifentanil in patients undergoing laparoscopic gynecologic surgery, continuous infusion of low dose ketamine decreased early postoperative pain and the quantity of opioids used.
Keywords: Hyperalgesia; Ketamine; Postoperative pain; Remifentanil; Sevoflurane.
Figures

References
-
- Thompson JP, Rowbotham DJ. Remifentanil--an opioid for the 21st century. Br J Anaesth. 1996;76:341–343. - PubMed
-
- Guignard B, Bossard AE, Coste C, Sessler DI, Lebrault C, Alfonsi P, et al. Acute opioid tolerance: intraoperative remifentanil increases postoperative pain and morphine requirement. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:409–417. - PubMed
-
- Vinik HR, Kissin I. Rapid development of tolerance to analgesia during remifentanil infusion in humans. Anesth Analg. 1998;86:1307–1311. - PubMed
-
- Angst MS, Koppert W, Pahl I, Clark DJ, Schmelz M. Short-term infusion of the mu-opioid agonist remifentanil in humans causes hyperalgesia during withdrawal. Pain. 2003;106:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Derrode N, Lebrun F, Levron JC, Chauvin M, Debaene B. Influence of peroperative opioid on postoperative pain after major abdominal surgery: sufentanil TCI versus remifentanil TCI. A randomized, controlled study. Br J Anaesth. 2003;91:842–849. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

