Cardiovascular oscillations at the bedside: early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis using heart rate characteristics monitoring
- PMID: 22026974
- PMCID: PMC4898648
- DOI: 10.1088/0967-3334/32/11/S08
Cardiovascular oscillations at the bedside: early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis using heart rate characteristics monitoring
Abstract
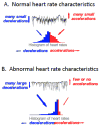
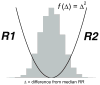
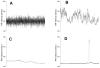
We have applied principles of statistical signal processing and nonlinear dynamics to analyze heart rate time series from premature newborn infants in order to assist in the early diagnosis of sepsis, a common and potentially deadly bacterial infection of the bloodstream. We began with the observation of reduced variability and transient decelerations in heart rate interval time series for hours up to days prior to clinical signs of illness. We find that measurements of standard deviation, sample asymmetry and sample entropy are highly related to imminent clinical illness. We developed multivariable statistical predictive models, and an interface to display the real-time results to clinicians. Using this approach, we have observed numerous cases in which incipient neonatal sepsis was diagnosed and treated without any clinical illness at all. This review focuses on the mathematical and statistical time series approaches used to detect these abnormal heart rate characteristics and present predictive monitoring information to the clinician.
Figures



References
-
- Aghili AA, Rizwan u, Griffin MP, Moorman JR. Scaling and ordering of neonatal heart rate variability. Phys Rev Lett. 1995;74:1254–1257. - PubMed
-
- Akselrod S, Gordon D, Ubel FA, Shannon DC, Barger AC, Cohen RJ. Power spectrum analysis of heart rate fluctuation: a quantitative probe of beat-to-beat cardiovascular control. Science. 1981;213:220–222. - PubMed
-
- Bendat JS, Piersol AG. Random data: Analysis and measurement procedures. New York: John Wiley; 1986. p. 566.
-
- Berger RD, Akselrod S, Gordon D, Cohen RJ. An efficient algorithm for spectral analysis of heart rate variability. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering. 1986;BME-33:900–904. - PubMed
-
- Brown TE, Beightol LA, Koh J, Eckberg DL. Important influence of respiration on human R-R interval power spectra is largely ignored. Journal of Applied Physiology. 1993;75:2310–2317. - PubMed
