Muscarinic receptor agonists stimulate matrix metalloproteinase 1-dependent invasion of human colon cancer cells
- PMID: 22027145
- PMCID: PMC3221914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.10.052
Muscarinic receptor agonists stimulate matrix metalloproteinase 1-dependent invasion of human colon cancer cells
Abstract
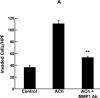
Mammalian matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) which degrade extracellular matrix facilitate colon cancer cell invasion into the bloodstream and extra-colonic tissues; in particular, MMP1 expression correlates strongly with advanced colon cancer stage, hematogenous metastasis and poor prognosis. Likewise, muscarinic receptor signaling plays an important role in colon cancer; muscarinic receptors are over-expressed in colon cancer compared to normal colon epithelial cells. Muscarinic receptor activation stimulates proliferation, migration and invasion of human colon cancer cells. In mouse intestinal neoplasia models genetic ablation of muscarinic receptors attenuates carcinogenesis. In the present work, we sought to link these observations by showing that MMP1 expression and activation plays a mechanistic role in muscarinic receptor agonist-induced colon cancer cell invasion. We show that acetylcholine, which robustly increases MMP1 expression, stimulates invasion of HT29 and H508 human colon cancer cells into human umbilical vein endothelial cell monolayers - this was abolished by pre-incubation with atropine, a non-selective muscarinic receptor inhibitor, and by pre-incubation with anti-MMP1 neutralizing antibody. Similar results were obtained using a Matrigel chamber assay and deoxycholyltaurine (DCT), an amidated dihydroxy bile acid associated with colon neoplasia in animal models and humans, and previously shown to interact functionally with muscarinic receptors. DCT treatment of human colon cancer cells resulted in time-dependent, 10-fold increased MMP1 expression, and DCT-induced cell invasion was also blocked by pre-treatment with anti-MMP1 antibody. This study contributes to understanding mechanisms underlying muscarinic receptor agonist-induced promotion of colon cancer and, more importantly, indicates that blocking MMP1 expression and activation has therapeutic promise to stop or retard colon cancer invasion and dissemination.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Overcoming Obstacles to Targeting Muscarinic Receptor Signaling in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 13;22(2):716. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020716. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33450835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscarinic receptor agonists stimulate human colon cancer cell migration and invasion.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):G749-60. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00306.2010. Epub 2011 Jan 27. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21273532 Free PMC article.
-
Interacting post-muscarinic receptor signaling pathways potentiate matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression and invasion of human colon cancer cells.Biochem J. 2017 Feb 20;474(5):647-665. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160704. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28008134 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-7-catalyzed release of HB-EGF mediates deoxycholyltaurine-induced proliferation of a human colon cancer cell line.Biochem Pharmacol. 2007 Apr 1;73(7):1001-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.11.028. Epub 2006 Dec 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17222808 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting M3 Muscarinic Receptors for Colon Cancer Therapy.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018;11(3):184-190. doi: 10.2174/1874467211666180119115828. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29357811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bile acid: a potential inducer of colon cancer stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016 Dec 1;7(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s13287-016-0439-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27908290 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in colitis-associated cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 15;13:1325095. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1325095. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38288108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arecoline Promotes Migration of A549 Lung Cancer Cells through Activating the EGFR/Src/FAK Pathway.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Mar 28;11(4):185. doi: 10.3390/toxins11040185. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30925742 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc finger protein 277 is an intestinal transit-amplifying cell marker and colon cancer oncogene.JCI Insight. 2022 Feb 22;7(4):e150894. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.150894. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35015732 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming Obstacles to Targeting Muscarinic Receptor Signaling in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 13;22(2):716. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020716. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33450835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Westermarck J, Kahari VM. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression in tumor invasion. FASEB J. 1999;13:781–792. - PubMed
-
- Zucker S, Vacirca J. Role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004;23:101–117. - PubMed
-
- Murray GI, Duncan ME, O'Neil P, Melvin WT, Fothergill JE. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Nat Med. 1996;2:461–462. - PubMed
-
- Baker EA, Bergin FG, Leaper DJ. Matrix metalloproteinases, their tissue inhibitors and colorectal cancer staging. Br J Surg. 2000;87:1215–1221. - PubMed
-
- Sunami E, Tsuno N, Osada T, Saito S, Kitayama J, Tomozawa S, Tsuruo T, Shibata Y, Muto T, Nagawa H. MMP-1 is a prognostic marker for hematogenous metastasis of colorectal cancer. Oncologist. 2000;5:108–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA120407/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK080843/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA107345/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-120407/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK-081479/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA-107345/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK089130/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-089130/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK077137/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-077137/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-080843/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK081479/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK-067872/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK067872/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

