Microarray analysis of peripheral blood lymphocytes from ALS patients and the SAFE detection of the KEGG ALS pathway
- PMID: 22027401
- PMCID: PMC3219589
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-4-74
Microarray analysis of peripheral blood lymphocytes from ALS patients and the SAFE detection of the KEGG ALS pathway
Abstract
Background: Sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (sALS) is a motor neuron disease with poorly understood etiology. Results of gene expression profiling studies of whole blood from ALS patients have not been validated and are difficult to relate to ALS pathogenesis because gene expression profiles depend on the relative abundance of the different cell types present in whole blood. We conducted microarray analyses using Agilent Human Whole Genome 4 × 44k Arrays on a more homogeneous cell population, namely purified peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs), from ALS patients and healthy controls to identify molecular signatures possibly relevant to ALS pathogenesis.
Methods: Differentially expressed genes were determined by LIMMA (Linear Models for MicroArray) and SAM (Significance Analysis of Microarrays) analyses. The SAFE (Significance Analysis of Function and Expression) procedure was used to identify molecular pathway perturbations. Proteasome inhibition assays were conducted on cultured peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from ALS patients to confirm alteration of the Ubiquitin/Proteasome System (UPS).
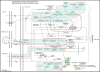
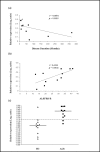
Results: For the first time, using SAFE in a global gene ontology analysis (gene set size 5-100), we show significant perturbation of the KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) ALS pathway of motor neuron degeneration in PBLs from ALS patients. This was the only KEGG disease pathway significantly upregulated among 25, and contributing genes, including SOD1, represented 54% of the encoded proteins or protein complexes of the KEGG ALS pathway. Further SAFE analysis, including gene set sizes >100, showed that only neurodegenerative diseases (4 out of 34 disease pathways) including ALS were significantly upregulated. Changes in UBR2 expression correlated inversely with time since onset of disease and directly with ALSFRS-R, implying that UBR2 was increased early in the course of ALS. Cultured PBMCs from ALS patients accumulated more ubiquitinated proteins than PBMCs from healthy controls in a serum-dependent manner confirming changes in this pathway.
Conclusions: Our study indicates that PBLs from sALS patients are strong responders to systemic signals or local signals acquired by cell trafficking, representing changes in gene expression similar to those present in brain and spinal cord of sALS patients. PBLs may provide a useful means to study ALS pathogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Bodansky A, Kim JM, Tempest L, Velagapudi A, Libby R, Ravits J. TDP-43 and ubiquitinated cytoplasmic aggregates in sporadic ALS are low frequency and widely distributed in the lower motor neuron columns independent of disease spread. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2010;11(3):321–327. doi: 10.3109/17482961003602363. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Es MA, Veldink JH, Saris CG, Blauw HM, van Vught PW, Birve A, Lemmens R, Schelhaas HJ, Groen EJ, Huisman MH, van der Kooi AJ, de Visser M, Dahlberg C, Estrada K, Rivadeneira F, Hofman A, Zwarts MJ, van Doormaal PT, Rujescu D, Strengman E, Giegling I, Muglia P, Tomik B, Slowik A, Uitterlinden AG, Hendrich C, Waibel S, Meyer T, Ludolph AC, Glass JD. et al.Genome-wide association study identifies 19p13.3 (UNC13A) and 9p21.2 as susceptibility loci for sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet. 2009;41(10):1083–1087. doi: 10.1038/ng.442. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Es MA, van Vught PW, Blauw HM, Franke L, Saris CG, Andersen PM, van den Bosch L, de Jong SW, van't Slot R, Birve A, Lemmens R, de Jong V, Baas F, Schelhaas HJ, Sleegers K, van Broeckhoven C, Wokke JH, Wijmenga C, Robberecht W, Veldink JH, Ophoff RA, van den Berg LH. ITPR2 as a susceptibility gene in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a genome-wide association study. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6(10):869–77. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70222-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Es MA, van Vught PW, Veldink JH, Andersen PM, Birve A, Lemmens R, Cronin S, van der Kooi AJ, de Visser M, Schelhaas HJ, Hardiman O, Ragoussis I, Lambrechts D, Robberecht W, Wokke JH, Ophoff RA, van den Berg LH. Analysis of FGGY as a risk factor for sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2009;10(5-6):441–7. doi: 10.3109/17482960802673042. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Es MA, van Vught PW, Blauw HM, Franke L, Saris CG, van den Bosch L, de Jong SW, de Jong V, Baas F, van't Slot R, Lemmens R, Schelhaas HJ, Birve A, Sleegers K, van Broeckhoven C, Schymick JC, Traynor BJ, Wokke JH, Wijmenga C, Robberecht W, Andersen PM, Veldink JH, Ophoff RA, van den Berg LH. Genetic variation in DPP6 is associated with susceptibility to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet. 2008;40(1):29–31. doi: 10.1038/ng.2007.52. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

