Participation of blood vessel cells in human adaptive immune responses
- PMID: 22030237
- PMCID: PMC3253953
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2011.09.006
Participation of blood vessel cells in human adaptive immune responses
Abstract
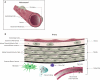
Circulating T cells contact blood vessels either when they extravasate across the walls of microvessels into inflamed tissues or when they enter into the walls of larger vessels in inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis. The blood vessel wall is largely composed of three cell types: endothelial cells lining the entire vascular tree; pericytes supporting the endothelium of microvessels; and smooth muscle cells forming the bulk of large vessel walls. Each of these cell types interacts with and alters the behavior of infiltrating T cells in different ways, making these cells active participants in the processes of immune-mediated inflammation. In this review, we compare and contrast what is known about the nature of these interactions in humans.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Fabre JW. Rat kidney allograft model: was it all too good to be true? Transplantation. 1982;34:223–225. - PubMed
-
- von Willebrand E, et al. Distribution of the major histocompatibility complex antigens in human and rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1985;27:616–621. - PubMed
-
- Pober JS, et al. Lymphocytes recognize human vascular endothelial and dermal fibroblast Ia antigens induced by recombinant immune interferon. Nature. 1983;305:726–729. - PubMed
-
- Tellides G, et al. Interferon-gamma elicits arteriosclerosis in the absence of leukocytes. Nature. 2000;403:207–211. - PubMed
-
- Ma W, et al. Interferon-gamma rapidly increases peptide transporter (TAP) subunit expression and peptide transport capacity in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:16585–16590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

