Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Israel: dissemination of global clones and unique features
- PMID: 22031705
- PMCID: PMC3256713
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.05446-11
Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Israel: dissemination of global clones and unique features
Abstract
From 2006 to 2009, 315 clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates were collected from 5 hospitals across Israel. Most isolates (64%) were related to the global clones spa types t001-SCCmec-I (SCCmec-I stands for staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type I) (n = 99; 31%), t002-SCCmec-II (n = 82; 26%), and t008-SCCmec-IV (n = 21; 7%), five of which were identified as MRSA strain USA-300. Seventeen strains unique to Israel were identified. SCCmec types IV and V were common among hospital-acquired isolates.
Figures
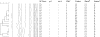
References
-
- Alon D, Abd-Elkadir F, Chowers M, Paitan Y. 2011. MRSA SCCmec epidemiology in Israel: development and implementation of an MRSA SCCmec typing strategy. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 30:1443–1452 - PubMed
-
- Alp E, et al. 2009. MRSA genotypes in Turkey: persistence over 10 years of a single clone of ST239. J. Infect. 58:433–438 - PubMed
-
- Borg MA, et al. 2007. Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in invasive isolates from southern and eastern Mediterranean countries. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 60:1310–1315 - PubMed
-
- Chen F-J, Hiramatsu K, Huang I-W, Wang C-H, Lauderdale T-LY. 2009. Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL)-positive methicillin-susceptible and resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Taiwan: identification of oxacillin-susceptible mecA-positive methicillin-resistant S. aureus. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 65:351–357 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

