ASXL1 mutations identify a high-risk subgroup of older patients with primary cytogenetically normal AML within the ELN Favorable genetic category
- PMID: 22031865
- PMCID: PMC3245212
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-08-368225
ASXL1 mutations identify a high-risk subgroup of older patients with primary cytogenetically normal AML within the ELN Favorable genetic category
Abstract
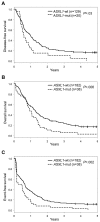
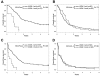
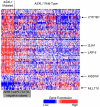
The associations of mutations in the enhancer of trithorax and polycomb family gene ASXL1 with pretreatment patient characteristics, outcomes, and gene-/microRNA-expression profiles in primary cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia (CN-AML) are unknown. We analyzed 423 adult patients for ASXL1 mutations, other prognostic gene mutations, and gene-/microRNA-expression profiles. ASXL1 mutations were 5 times more common in older (≥ 60 years) patients (16.2%) than those younger than 60 years (3.2%; P < .001). Among older patients, ASXL1 mutations associated with wild-type NPM1 (P < .001), absence of FLT3-internal tandem duplications (P = .002), mutated CEBPA (P = .01), and with inferior complete remission (CR) rate (P = .04), disease-free survival (DFS; P = .03), overall survival (OS; P = .006), and event-free survival (EFS; P = .002). Within the European LeukemiaNet (ELN) genetic categories of older CN-AML, ASXL1 mutations associated with inferior CR rate (P = .02), OS (P < .001), and EFS (P < .001) among ELN Favorable, but not among ELN Intermediate-I patients. Multivariable analyses confirmed associations of ASXL1 mutations with unfavorable CR rate (P = .03), DFS (P < .001), OS (P < .001), and EFS (P < .001) among ELN Favorable patients. We identified an ASXL1 mutation-associated gene-expression signature, but no microRNA-expression signature. This first study of ASXL1 mutations in primary CN-AML demonstrates that ASXL1-mutated older patients, particularly within the ELN Favorable group, have unfavorable outcomes and may be candidates for experimental treatment approaches.
Figures

References
-
- Fisher CL, Randazzo F, Humphries RK, Brock HW. Characterization of Asxl1, a murine homolog of Additional sex combs, and analysis of the Asx-like gene family. Gene. 2006;369:109–118. - PubMed
-
- Gelsi-Boyer V, Trouplin V, Adélaïde J, et al. Mutations of polycomb-associated gene ASXL1 in myelodysplastic syndromes and chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2009;145(6):788–800. - PubMed
-
- Carbuccia N, Murati A, Trouplin V, et al. Mutations of ASXL1 gene in myeloproliferative neoplasms [letter]. Leukemia. 2009;23(11):2183–2186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA41287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA033601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA114725/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA101140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA041287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA31946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA140158/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA33601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA140158/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA101140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA129657/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA129657/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA114725/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

