Evaluation of the diagnostic indices and clinical utility of qualitative cardiodetect® test kit in diagnosis of ami within 12 hours of onset of chest pain in the emergency department
- PMID: 22032555
- PMCID: PMC3219693
- DOI: 10.1186/1865-1380-4-67
Evaluation of the diagnostic indices and clinical utility of qualitative cardiodetect® test kit in diagnosis of ami within 12 hours of onset of chest pain in the emergency department
Abstract
Introduction: Cardiac biomarkers may be invaluable in establishing the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in the ED setting.
Objective: To assess the diagnostic indices of the Cardio Detect assay and the quantitative cardiac troponin T test, in diagnosing AMI in the ED, according to the time of onset of chest pain.
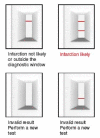
Methodology: A total of 80 eligible patients presenting with ischemic type chest pain with duration of symptoms within the last 36 h were enrolled. All patients were tested for H-FABP and troponin T at presentation to the ED. A repeated Cardio Detect test was performed 1 h after the initial negative result, and a repeated troponin T test was also performed 8-12 h after an initial negative result. The diagnostic indices [sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, receiver operating curve (ROC)] were analyzed for Cardio Detect and Troponin T (individually and in combination) and also for the repeat Cardio Detect test. Data entry and analysis were performed using SPSS version 12.0 and Analyze-it software.
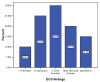
Results: The Cardio Detect test was more sensitive and had a higher NPV than the troponin T (TnT) test during the first 12 h of onset of chest pain. The repeat Cardio Detect had better sensitivity and NPV than the initial Cardio Detect. The sensitivity and NPV of the combination test (Cardio Detect and troponin T) were also superior to each test performed individually.
Conclusion: The Cardio Detect test is more sensitive and has a better NPV than the troponin T test during the first 12 h of AMI. It may be used to rule out myocardial infarction during the early phase of ischemic chest pain.
Figures
References
-
- Hasche ET, Fernandes C, Freedman SB, Jeremy RW. Relation between ischemia time, infarct size, and left ventricular function in humans. Circulation. 1995;92(4):710–719. - PubMed
-
- HA Guideline for CPR and ECC 2005 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Part 8: Stabilization of the patient with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2005;112(24_suppl):IV–89-110.
-
- Altman D, Machin D, Bryant Trevor N, Gardner MJ. Statistics with confidence; confidence interval and statistical guidelines. 2. BMJ books; 2000. - PubMed
-
- Malaysian CPG on STEMI. Malaysian Clinical Practice Guideline on ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. 2 2007.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources