Pyogenic spondylitis
- PMID: 22033610
- PMCID: PMC3282872
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-011-1384-6
Pyogenic spondylitis
Abstract
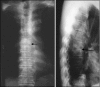
Pyogenic spondylitis is a neurological and life threatening condition. It encompasses a broad range of clinical entities, including pyogenic spondylodiscitis, septic discitis, vertebral osteomyelitis, and epidural abscess. The incidence though low appears to be on the rise. The diagnosis is based on clinical, radiological, blood and tissue cultures and histopathological findings. Most of the cases can be treated non-operatively. Surgical treatment is required in 10-20% of patients. Anterior decompression, debridement and fusion are generally recommended and instrumentation is acceptable after good surgical debridement with postoperative antibiotic cover.
Figures


References
-
- MacDonald JW. Management of spinal infection. Curr Orthop. 2002;16:462–470. doi: 10.1054/cuor.2002.0249. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

