Single-shot turbo spin-echo diffusion-weighted imaging for retinoblastoma: initial experience
- PMID: 22033715
- PMCID: PMC7966176
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2729
Single-shot turbo spin-echo diffusion-weighted imaging for retinoblastoma: initial experience
Abstract
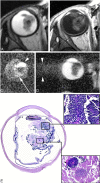
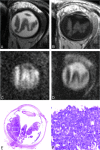
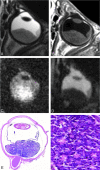
Background and purpose: Retinoblastoma may exhibit variable hyperintensities on DWI, resulting in different values in the ADC maps, depending on their histology and cellularity. However, EP-based DWI has susceptibility artifacts and image distortions, which make DWI of the orbit a challenging technique. The aim of this study was to investigate the feasibility of single-shot turbo spin-echo (HASTE) DWI in the evaluation of children with retinoblastoma and to assess the value of ADC maps in differentiating viable and necrotic tumor tissue.
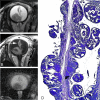
Materials and methods: Two radiologists assessed conventional MR images, DWI, and ADC maps of 17 patients with retinoblastoma (n = 17 eyes). Non-EP DWI was performed by using a HASTE sequence with b-values of 0 and 1000 s/mm(2). ADC values were measured for enhancing and nonenhancing tumor tissue. ADC maps were compared with histopathologic findings regarding tumor differentiation and viability.
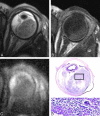
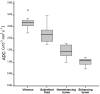
Results: On DWI, vital tumor tissue showed hyperintensity with negligible intensity of surrounding vitreous. The difference in mean (range) ADC values between enhancing (1.03 [0.72-1.22] × 10(-3) mm(2) s(-1)) and nonenhancing (1.47 [0.99-1.80] × 10(-3) mm(2) s(-1)) parts of retinoblastoma was statistically significant (P < .0005). Nonenhancing tumor parts showed a significantly lower ADC compared with vitreous (2.67 [2.24-3.20]×10(-3) mm(2) s(-1)) (P < .0005) and subretinal fluid (2.20 [1.76-2.96] × 10(-3) mm(2) s(-1)) (P < .0005). Histopathologically, low ADC values (enhancing tumor part) correlated to viable tumor tissue, whereas intermediate ADC values (nonenhancing tumor parts) correlated to necrotic tumor tissue.
Conclusions: HASTE DWI allowed adequate characterization of retinoblastoma, and ADC is a helpful tool to differentiate viable and necrotic tumor tissue and might be valuable in monitoring the response to eye-preserving therapies.
Figures
References
-
- de Graaf P, Barkhof F, Moll AC, et al. Retinoblastoma: MR imaging parameters in detection of tumor extent. Radiology 2005;235:197–207 - PubMed
-
- Brisse HJ, Guesmi M, Aerts I, et al. Relevance of CT and MRI in retinoblastoma for the diagnosis of postlaminar invasion with normal-size optic nerve: a retrospective study of 150 patients with histological comparison. Pediatr Radiol 2007;37:649–56 - PubMed
-
- Lemke AJ, Kazi I, Mergner U, et al. Retinoblastoma: MR appearance using a surface coil in comparison with histopathological results. Eur Radiol 2007;17:49–60 - PubMed
-
- Apushkin MA, Apushkin MA, Shapiro MJ, et al. Retinoblastoma and simulating lesions: role of imaging. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2005;15:49–67 - PubMed
-
- Vahedi A, Lumbroso-Le Rouic L, Levy Gabriel C, et al. Differential diagnosis of retinoblastoma: a retrospective study of 486 cases. J Fr Ophtalmol 2008;31:165–72 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
