JCV agnoprotein-induced reduction in CXCL5/LIX secretion by oligodendrocytes is associated with activation of apoptotic signaling in neurons
- PMID: 22034072
- PMCID: PMC3296900
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.23065
JCV agnoprotein-induced reduction in CXCL5/LIX secretion by oligodendrocytes is associated with activation of apoptotic signaling in neurons
Abstract
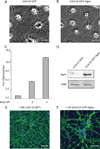
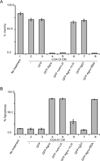
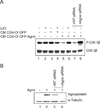
An indispensable role for oligodendrocytes in the protection of axon function and promotion of neuronal survival is strongly supported by the finding of progressive neuron/axon degeneration in human neurological diseases that affect oligodendrocytes. Imaging and pathological studies of the CNS have shown the presence of neuroaxonal injury in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), a demyelinating disease of the CNS, resulting from destruction of oligodendrocytes upon productive replication of the pathogenic neurotropic polyomavirus JC. Here, we examined the extracellular factors involved in communication between oligodendrocytes and neurons. Culturing cortical neurons with conditioned medium (CM) from rat CG4 oligodendrocytic cells that express the JCV agnoprotein showed that CXCL5/LIX, which is a chemokine closely related to the human CXCL5/ENA78 and CXCL6/GCP-2 chemokines, is essential for neuronal cell survival. We found that in CM from agnoprotein-producing CG-4 cells level of CXC5/LIX is decreased compared to control cells. We also demonstrated that a reduced expression of CXCL5/LIX by CG4 GFP-Agno cells triggered a cascade of signaling events in cortical neurons. Analysis of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and glycogen synthase kinase (GSK3) pathways showed that they are involved in mechanisms of neuronal apoptosis in response to the depletion of CXCL5/LIX signaling. These data suggest that agnoprotein-induced dysregulation of chemokine production by oligodendrocytes may contribute to neuronal/axonal injury in the pathogenesis of PML lesions.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Atta UR, Harvey K, Siddiqui RA. Interleukin-8: an autocrine inflammatory mediator. Curr Pharm Des. 1999;5:241–253. - PubMed
-
- Bajetto A, Bonavia R, Barbero S, Schettini G. Characterization of chemokines and their receptors in the central nervous system: physiopathological implications. J. Neurochem. 2002;82:1311–1329. - PubMed
-
- Berger JR, Kaszovitz B, Post MJ, Dickinson G. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. A review of the literature with a report of sixteen cases. Ann. Intern Med. 1987;107:78–87. - PubMed
-
- Berger JR, Houff S. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: lessons from AIDS and natalizumab. Neurol Res. 2006;28:299–305. - PubMed
-
- Berger JR. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2007;7:461–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

