Clinical application of a rapid microbiological test based on capillary zone electrophoresis to assess local skin infection
- PMID: 22035265
- PMCID: PMC3219748
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-467
Clinical application of a rapid microbiological test based on capillary zone electrophoresis to assess local skin infection
Abstract
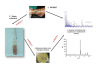
Background: The basic clinical problem associated with infection treatment is the fact that classic, commonly and routinely used isolation and identification methods are based on long-term processes of a phenotypic analysis of microorganisms. Consequently sometimes, especially in small centres, rapid implementation of antibacterial treatment becomes delayed.The work presents the initial results of rapid microbiological identification based on an original method of capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE). The study involved the analysis of 78 biological samples from post-operative wounds and trophic ulcers.
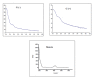
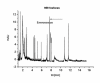
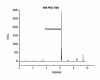
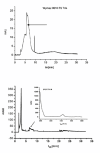
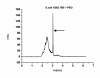
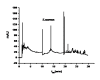
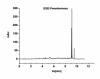
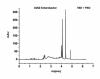
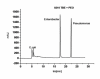
Results: The attempt was made to identify individual bacterial species based on characteristic features of electropherograms achieved. Finally, G(+) cocci type bacteria and different G(-) rods were identified with sensitivity of 88.1% and specificity of 100%.
Conclusions: Based on the clinical trials using an electrophoretic technique in the field of microbiological diagnostics of infected exudate from a post-operative wound it can be concluded that it is a rapid and relatively sensitive method for initial identification of infectious pathogens.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The clinical use of a fast screening test based on technology of capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) for identification of Escherichia coli infection in biological material.Med Sci Monit. 2011 Oct;17(10):MT91-6. doi: 10.12659/msm.881967. Med Sci Monit. 2011. PMID: 21959622 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a specific marker for hepatitis C virus infection using capillary zone electrophoresis.Clin Chim Acta. 2004 Aug 16;346(2):171-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cccn.2004.03.024. Clin Chim Acta. 2004. PMID: 15256318
-
[Retrospective analysis of 2 997 inpatients with skin and soft tissue injuries].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020 Sep 20;36(9):821-829. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20200202-00036. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32972067 Chinese.
-
[Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry and its application to proteomic analysis].Se Pu. 2020 Oct 8;38(10):1117-1124. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.03005. Se Pu. 2020. PMID: 34213108 Review. Chinese.
-
Study of metallothionein using capillary zone electrophoresis.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002 Dec 5;781(1-2):303-11. doi: 10.1016/s1570-0232(02)00496-8. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 12450665 Review.
Cited by
-
The influence of different pH on the electrophoretic behaviour of Saccharomyces cerevisiae modified by calcium ions.Sci Rep. 2018 May 8;8(1):7261. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25024-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29739986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kadłubowski M, Skoczyńska A, Hryniewicz W. Rekomendacje diagnostyczne inwazyjnych zakażeń bakteryjnych nabytych poza szpitalem. KOROUN, NIL. 2007.
-
- Giedrys-Kalemba S. In: Podręcznik dla zespołów kontroli zakażeń. Red. nauk. Heczko P, Wójkowska-Mach J Wydaw, editor. Lekarskie PZWL; 2009. Typowanie molekularne w dochodzeniu epidemiologicznym. Zakażenia szpitalne; pp. 110–124. - PubMed
-
- Van Belkum A, Renders NHM, Smith S, Overbeek SE, Verbrugh HA. Comparison of conventional and molecular methods for the detection of bacterial pathogens in sputum samples from cystic fibrosis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2000;27:51–57. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Moore J, Murphy PG, Millar BC, Elborn JS. Early detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa - comparison of conventional versus molecular (PCR) detection directly from adult patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) Annals Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2004;3:21–26. doi: 10.1186/1476-0711-3-21. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

