Exploratory analysis of a phase III trial of pirfenidone identifies a subpopulation of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis as benefiting from treatment
- PMID: 22035508
- PMCID: PMC3216874
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-12-143
Exploratory analysis of a phase III trial of pirfenidone identifies a subpopulation of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis as benefiting from treatment
Abstract
Background: A phase III trial in Japan showed that pirfenidone is effective for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). To find out which patients specifically benefit from pirfenidone, we analyzed in an exploratory manner the data from the phase III trial.
Methods: The patients in the phase III trial were stratified by baseline percentage predicted vital capacity (%VC), arterial oxygen partial pressure (PaO(2)), and the lowest oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry (SpO(2)) during the 6-minute steady-state exercise test (6MET). In the subpopulations, changes in VC and subjective symptoms (cough and dyspnea on the Fletcher, Hugh-Jones [F, H-J] Classification scale) were evaluated in patients treated with high-dose (1800 mg/day) pirfenidone, low-dose (1200 mg/day) pirfenidone, and placebo at week 52.
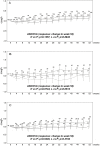
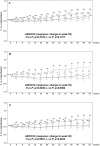
Results: Significant efficacy of pirfenidone in reducing the decline in VC could be seen in a subpopulation having %VC ≥ 70% and SpO(2) < 90% at baseline. This favorable effect was accompanied by categorical change in VC and progression-free survival time. In the subpopulation, pirfenidone significantly suppressed cough and dyspnea.
Conclusions: IPF patients having %VC ≥ 70% and SpO(2) < 90% at baseline will most likely benefit from pirfenidone when evaluated using changes in VC (and %VC), and cough and dyspnea symptoms. This subpopulation could expect to benefit most from pirfenidone treatment.
Trial registration: This clinical trial was registered with the Japan Pharmaceutical Information Center (JAPIC) on September 13th, 2005 (REGISTRATION NUMBER: JAPICCTI-050121).
Figures

References
-
- Bjoraker JA, Ryu JH, Edwin MK, Myers JL, Tazelaar HD, Schroeder DR, Offord KP. Prognostic significance of histopathologic subsets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:199–203. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz DA, Helmers RA, Galvin JR, Van Fossen DS, Frees KL, Dayton CS, Burmeister LF, Hunninghake GW. Determinants of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;149:450–454. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G, Johnson WC, Lockhart D, Mageto Y. Treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with a new antifibrotic agent, pirfenidone: results of a prospective, open-label Phase II study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;159:1061–1069. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

