Distal airway stem cells yield alveoli in vitro and during lung regeneration following H1N1 influenza infection
- PMID: 22036562
- PMCID: PMC4040224
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.001
Distal airway stem cells yield alveoli in vitro and during lung regeneration following H1N1 influenza infection
Abstract
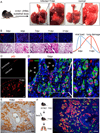
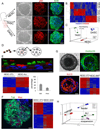
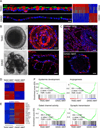
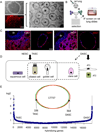
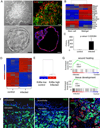
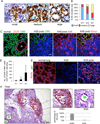
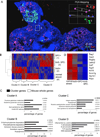
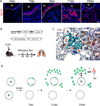
The extent of lung regeneration following catastrophic damage and the potential role of adult stem cells in such a process remains obscure. Sublethal infection of mice with an H1N1 influenza virus related to that of the 1918 pandemic triggers massive airway damage followed by apparent regeneration. We show here that p63-expressing stem cells in the bronchiolar epithelium undergo rapid proliferation after infection and radiate to interbronchiolar regions of alveolar ablation. Once there, these cells assemble into discrete, Krt5+ pods and initiate expression of markers typical of alveoli. Gene expression profiles of these pods suggest that they are intermediates in the reconstitution of the alveolar-capillary network eradicated by viral infection. The dynamics of this p63-expressing stem cell in lung regeneration mirrors our parallel finding that defined pedigrees of human distal airway stem cells assemble alveoli-like structures in vitro and suggests new therapeutic avenues to acute and chronic airway disease.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
A breath of fresh air in lung regeneration.Cell. 2011 Oct 28;147(3):485-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.008. Cell. 2011. PMID: 22036554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belser JA, Szretter KJ, Katz JM, Tumpey TM. Use of animal models to understand the pandemic potential of highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2009;73:55–97. - PubMed
-
- Eaton DC, Helms MN, Koval M, Bao HF, Jain L. The contribution of epithelial sodium channels to alveolar function in health and disease. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:403–423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

