A unified model of mammalian BCL-2 protein family interactions at the mitochondria
- PMID: 22036586
- PMCID: PMC3221787
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.10.001
A unified model of mammalian BCL-2 protein family interactions at the mitochondria
Abstract
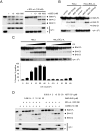
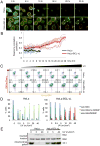
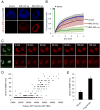
During apoptosis, the BCL-2 protein family controls mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), but the dynamics of this regulation remain controversial. We employed chimeric proteins composed of exogenous BH3 domains inserted into a tBID backbone that can activate the proapoptotic effectors BAX and BAK to permeabilize membranes without being universally sequestered by all antiapoptotic BCL-2 proteins. We thus identified two "modes" whereby prosurvival BCL-2 proteins can block MOMP, by sequestering direct-activator BH3-only proteins ("MODE 1") or by binding active BAX and BAK ("MODE 2"). Notably, we found that MODE 1 sequestration is less efficient and more easily derepressed to promote MOMP than MODE 2. Further, MODE 2 sequestration prevents mitochondrial fusion. We provide a unified model of BCL-2 family function that helps to explain otherwise paradoxical observations relating to MOMP, apoptosis, and mitochondrial dynamics.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
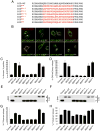
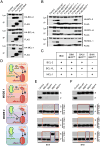
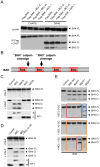
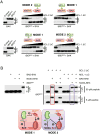
Comment in
-
Staying alive: defensive strategies in the BCL-2 family playbook.Mol Cell. 2011 Nov 18;44(4):509-10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.002. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 22099298
References
-
- Adler J, Parmryd I. Quantifying colocalization by correlation: the Pearson correlation coefficient is superior to the Mander’s overlap coefficient. Cytometry A. 2010;77:733–742. - PubMed
-
- Certo M, Del Gaizo Moore V, Nishino M, Wei G, Korsmeyer S, Armstrong SA, Letai A. Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:351–365. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Willis SN, Wei A, Smith BJ, Fletcher JI, Hinds MG, Colman PM, Day CL, Adams JM, Huang DCS. Differential targeting of prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins by their BH3-only ligands allows complementary apoptotic function. Molecular Cell. 2005;17:393–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

